Kubernetes
I am currently using Ubuntu 24.04 LTS on Raspberry Pi 5 for Kubernetes. As a first step1, extend the /boot/firmware/cmdline.txt with the following as a single line:
cgroup_enable=cpuset cgroup_enable=memory cgroup_memory=1 swapaccount=1
NOTE: This way, I’ve avoided the cgroup configuration2 via Kubernetes.
Install Dynamic IP
cri-dockerd
I found the default container communication in Ubuntu 24.04 is not the cir-docker and didn’t find the proper binaries to install. I used the cri-dockerd adapter to integrate Docker Engine with Kubernetes. Therefore, it is installed3 from the source. Install the necessary tools on all the machines:
# install make
sudo apt install make
# install go
sudo snap install go --classic
Clone the repository to all the machines
git clone https://github.com/Mirantis/cri-dockerd.git
Then, build and install
# Build
cd cri-dockerd
make cri-dockerd
# Installation
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/bin
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 cri-dockerd /usr/local/bin/cri-dockerd
activate the cri-docker for communication.
sudo install packaging/systemd/* /etc/systemd/system
sudo sed -i -e 's,/usr/bin/cri-dockerd,/usr/local/bin/cri-dockerd,' /etc/systemd/system/cri-docker.service
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable --now cri-docker.socket
Docker
To install
curl -sSL get.docker.com | sh
In addition to that, I added the user to the docker group: sudo usermod -aG docker oj
After installing the docker, enable the routing as follows:
Find the following line in the file /etc/sysctl.conf and uncomment
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
You can verify the docker installation by running docker run hello-world.
NOTE: You have to install docker for all the cluster nodes.
Kubeadm
Now you are ready to install the Kubeadm4 and, in this case, use the “Debian-based distributions”.
After installing Kubectl, add to the bash-completion
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
kubectl completion bash | sudo tee /etc/bash_completion.d/kubectl > /dev/null
Cluster
Find the routing before initiate cluster
ip route show
To create the cluster
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
As an output
kubeadm join 192.168.1.121:6443 --token f9zlr3.jrbkjy4gagp16ym7 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:43ae7ab6a144b1c5605ea6ae9715e0f491668df1e36091fda8067acdaeea40c4
As the above output stated
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Create network driver
sysctl net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1
Install for static IP
Allocate static IPs
Update the file /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml master and worker nodes for static IP (160 for master and 163 for worker) with the broadcasting via 192.168.1.255.
The Master ip is 192.168.1.160/29(within the range of 160 to 167)
network:
version: 2
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: false
dhcp6: false
addresses:
- '192.168.1.160/29'
optional: true
routes:
- to: 0.0.0.0/0
via: 192.168.1.255
wifis:
renderer: networkd
wlan0:
access-points:
TP-LINK_872B_5G:
password: <password already in>
dhcp4: true
optional: true
And the worker is
network:
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: no
dhcp6: no
optional: false
addresses:
- 192.168.1.11/24
routes:
- via: 192.168.1.1
to: default
nameservers:
addresses: [192.168.1.1]
version: 2
renderer: networkd
In the file /etc/sysctl.conf change the value of net.ipv4.ip_forward to 1.

Reboot after apply
sudo netplan apply
Install the docker
curl -sSL get.docker.com | sh
In addition to that, I added the user to the docker group: sudo usermod -aG docker oj
sudo containerd config default > /etc/containerd/config.toml
and change the value SystemdCgroup = true.
NOTE: I’ve got permission error. Therefore login as sudo su first.
and restart the service:
systemctl restart containerd
Install the kubernetes as explained in the above section.
Find the default gateway with
ip route show
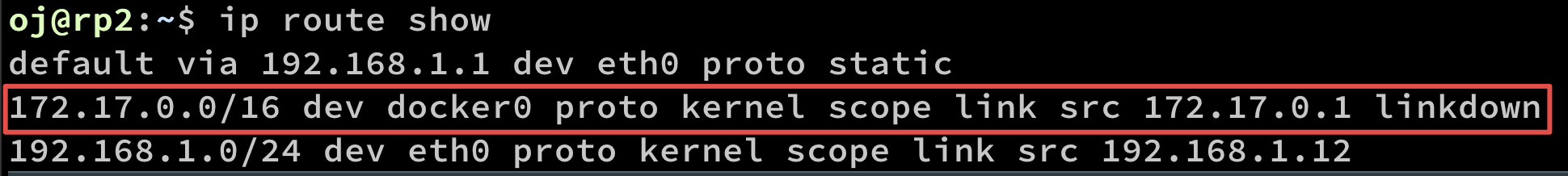
To create the cluster in the master
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.244.0.0/16 --apiserver-advertise-address 192.168.1.11 --control-plane-endpoint 192.168.1.11
To join the worker node
sudo kubeadm join 192.168.1.11:6443 --token 447r22.zx6qjx2tnt56ksu9 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:07db6cd942358d78d2a544d777e023f8a8f4b2aa50591e2f6b3b99cb1fc674d7
Then
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Network Layer 2 installation
use the fannel as the driver only on master
# no sudo need
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
Verify all the namespaces are running
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
To find all the running nodes
kubectl get nodes

If you use cri-dockerd, you have to install and activate the CRI in the worker nodes. After that join the worker to cluster, for example:
kubeadm join 192.168.1.121:6443 --token f9zlr3.jrbkjy4gagp16ym7 \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:43ae7ab6a144b1c5605ea6ae9715e0f491668df1e36091fda8067acdaeea40c4 --cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sock
The postfix
--cri-socket unix:///var/run/cri-dockerd.sockhas been added because you have to install and activate the crib on the worker nodes as well.
The output will be something similar to:
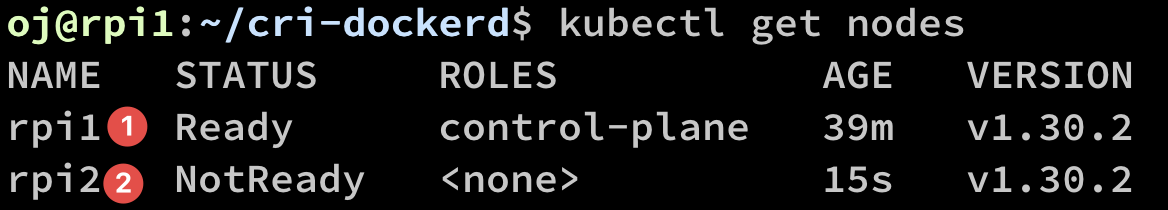
Command to verify the cluster
{ clear && \
echo -e "\n=== Kubernetes Status ===\n" && \
kubectl get --raw '/healthz?verbose' && \
kubectl version --short && \
kubectl get nodes && \
kubectl cluster-info;
} | grep -z 'Ready\| ok\|passed\|running'
Getting started
The simple diagnostic for the cluster
kubectl get componentstatuses
Output:
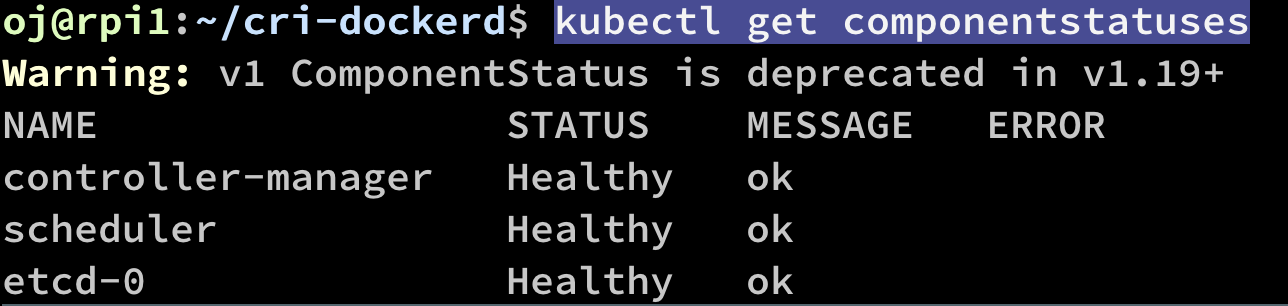
To get more information about nodes:
kubectl describe nodes rpi2
The Kubernetes proxy is responsible for routing network traffic to load-balanced services in the cluster. The proxy must be present on every node in the cluster. You can find the kube proxy under the kube-system namespace:
kubectl get daemonSets --namespace=kube-system
ouptput

To get the services
kubectl get services --namespace=kube-system kube-dns
Output where you can find the cluster IP:

Get the deployments to the cluster
kubectl get deployments --namespace=kube-system

To create a new namespace: stuff.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: mystuff
and run the command (1)
kubectl apply -f stuff.yaml
To create a pod on mystuff namespace (3):
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx:1.23.0 --restart=Never -n mystuff
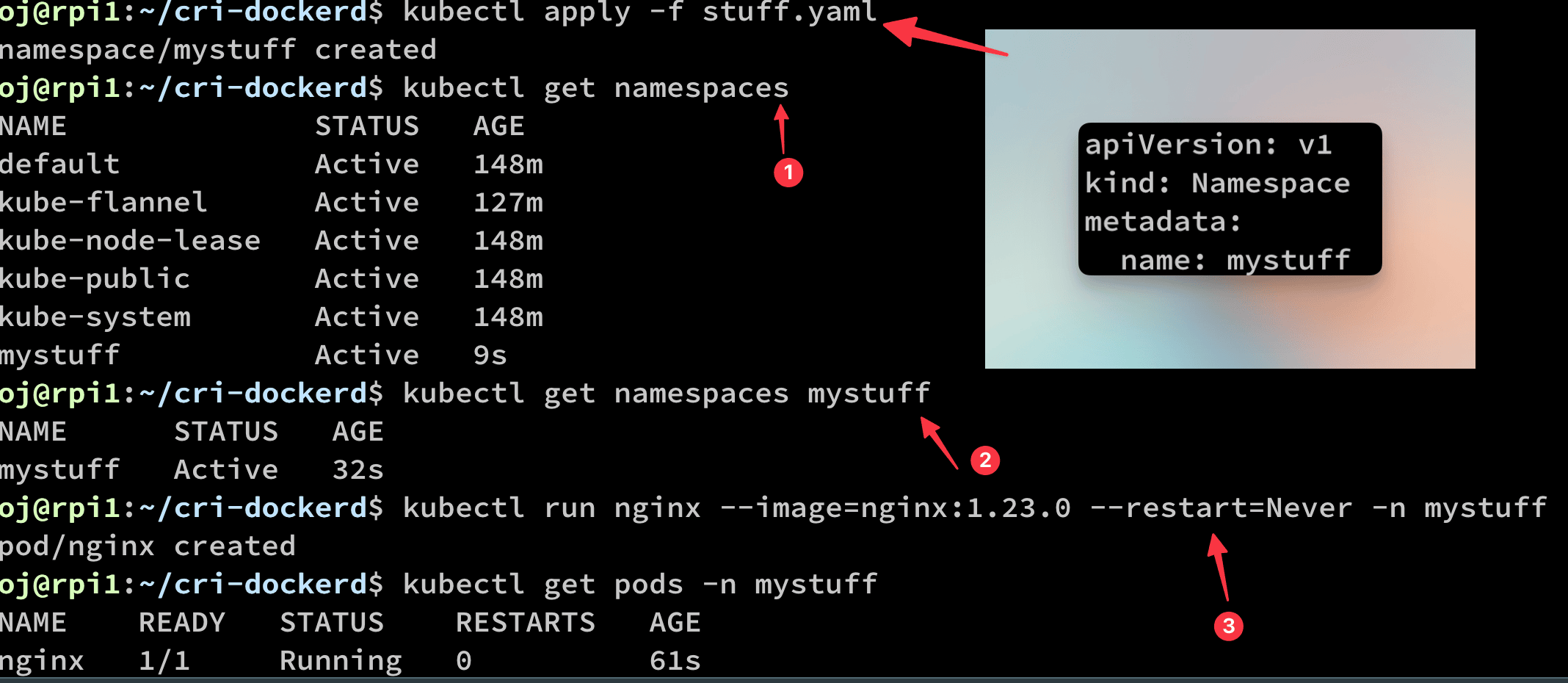
To change the default namespace:
kubectl config set-context my-context --namespace=mystuff
# use the context
kubectl config use-context my-context
Deploy
Declarative deployment (echoserver.yaml):
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
run: hello
name: hello
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
run: hello
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: hello
spec:
containers:
- image: registry.k8s.io/echoserver:1.9
name: hello
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
To deploy to cluster
kubectl apply -f echoserver.yaml
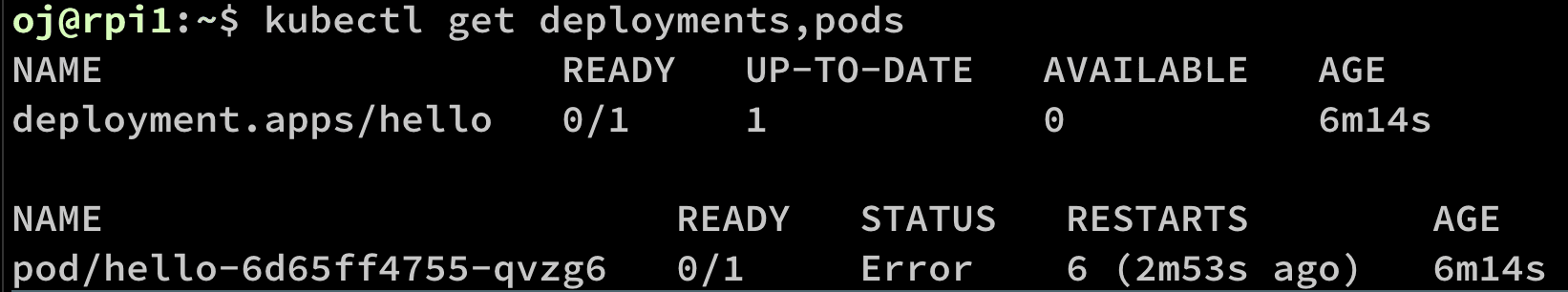
You have to expose the service before use (1)
kubectl expose deployment hello --type=NodePort
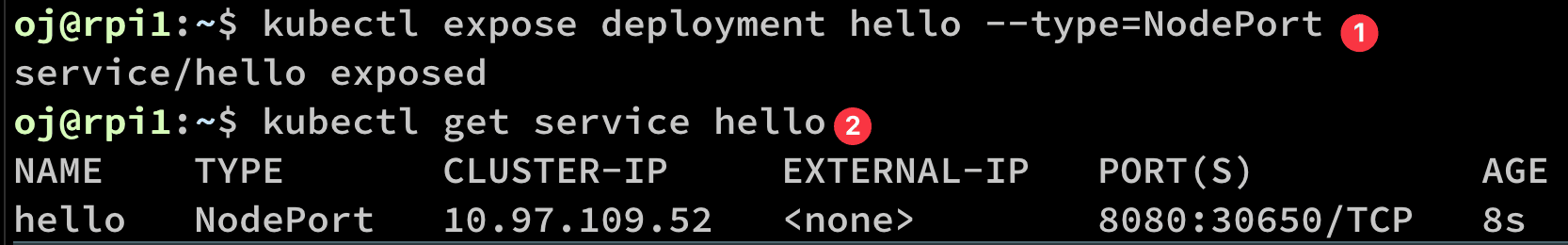
You can see the exactly mapped port (2).
if you want to change the port:
kubectl patch service hello --type='json' --patch='[{"op": "replace", "path": "/spec/ports/0/nodePort", "value":31001}]'
For more information: kubectl describe service hello
To scale the deployment:
kubectl scale deployment hello --replicas=1
To list that scaling
kubectl get pods -l run=hello
To get the list of running pods
kubectl get pods --selector=run=hello
To delete the pod
kubectl delete --now pod hello-6d65ff4755-qvzg6
To watch
watch kubectl get pods --selector=run=hello
General commands
Common
To describe the object
kubectl describe <resource-name> <obj-name>
For example,
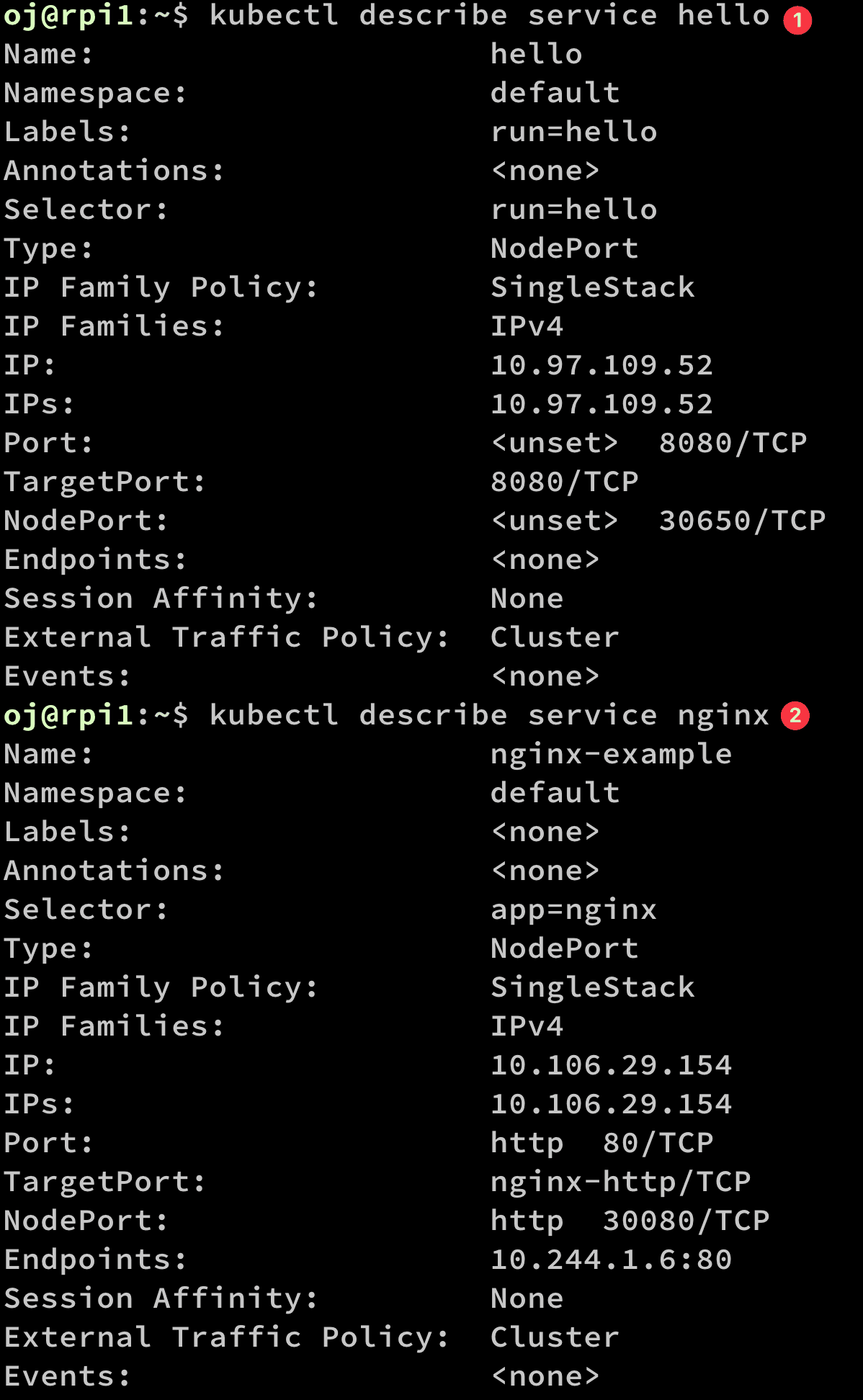
- Describe the
helloservice (which is to be deleted in the next) that is broken. - Describe the nginx, which is currently running without a problem (http://192.168.1.121:30080)
NOTE: From the NodePort value, you can find why
helloservice is not working
To delete the already deployed service
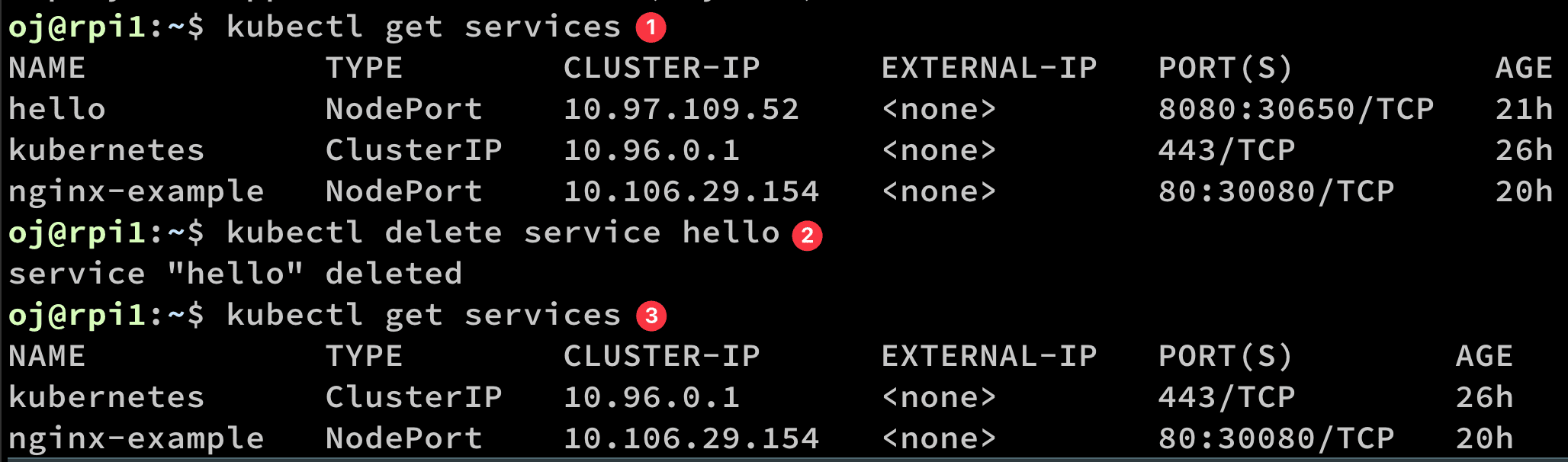
- List the services
- Delete the first of the list that is
hello - verify the service
hellowas deleted.
These records can be manipulated with the edit-last-applied, set-last-applied, and view-last-applied:
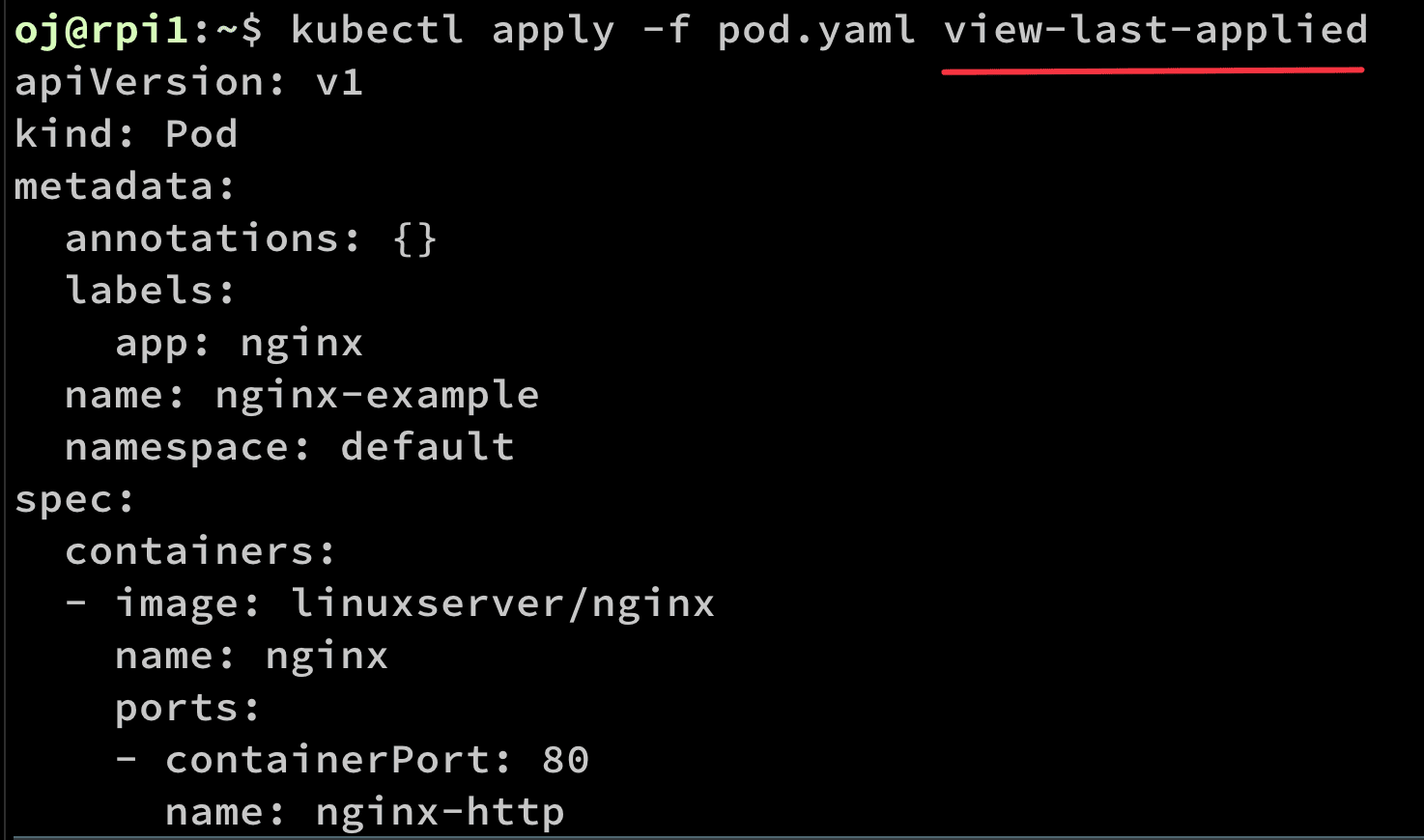
To label
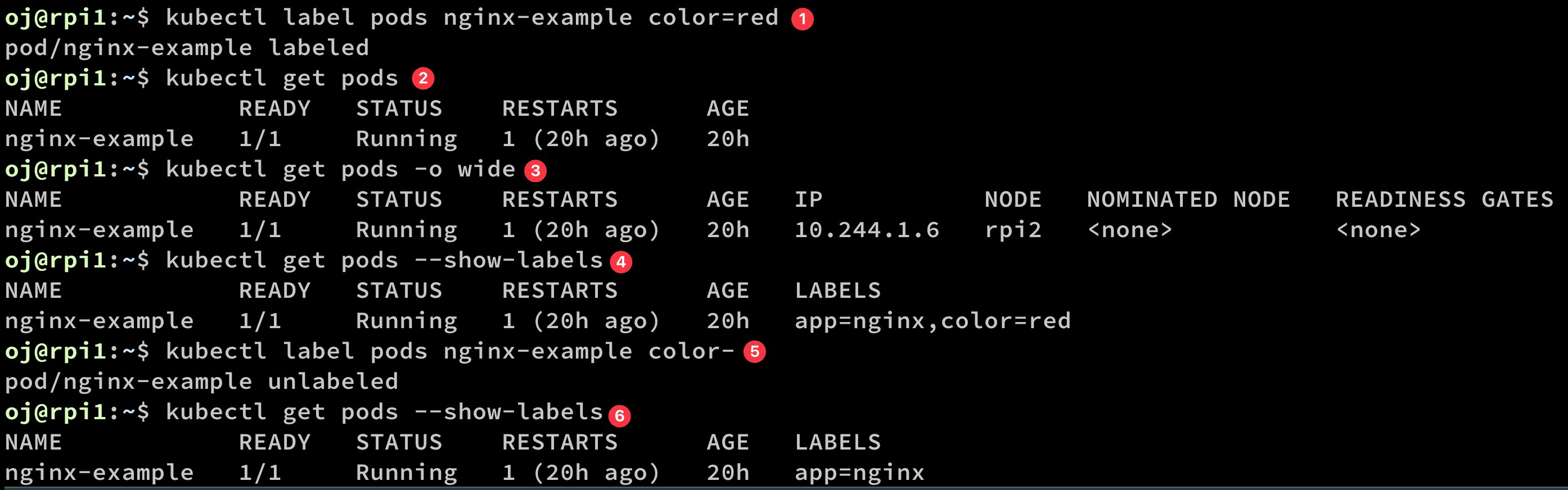
- Label the pod
nginx-example - Show the pods, but no label shows
- Show the pods in wider, but no label shows
- use the
--show-labels - remove the label
- confirm the label has been removed.
To see the logs kubectl logs <pod-name>
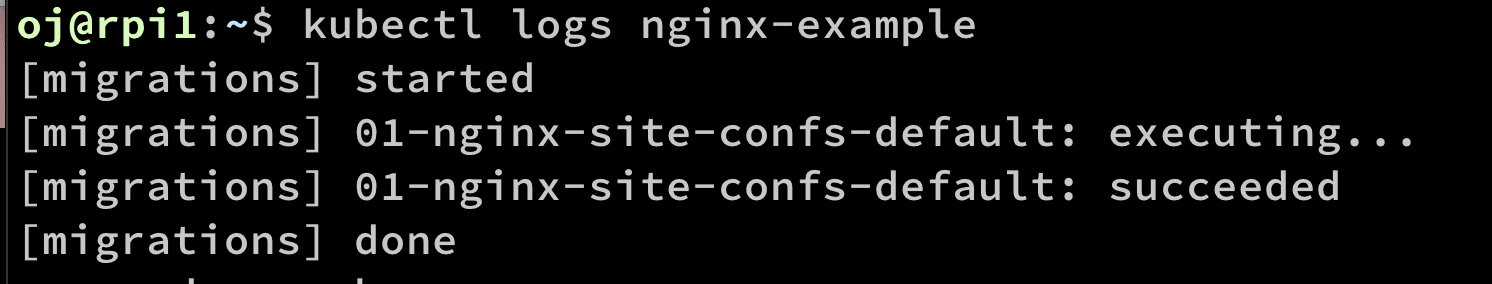
NOTE: If you have multiple containers in your Pod, use the
-cflag.
Login to the pod kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- bash with intractive shell

Note: The
attachcommand is similar toKubectl logsbut will allow you to send input to the running process.
copy files (reverse also possible)
kubectl cp </path/to/local/file> <pod-name>:</path/to/remote/file>

- create test.txt in the local machine
- list the local machine test.txt file
- copy local machine test.txt to the root of the nginx
- interactively log in to the nginx-example pod via bash
- List the files
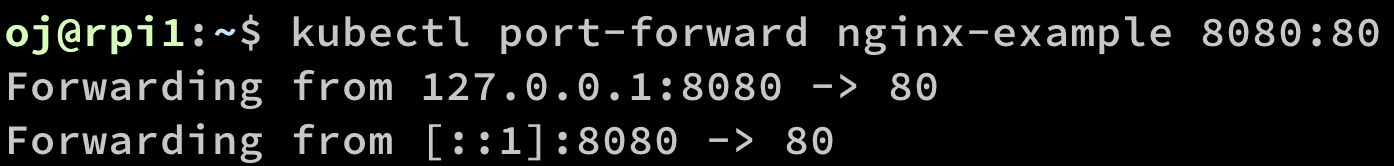
Port forwarding to access via local machine
kubectl port-forward <pod-name> <local machine port>:<remote container>
Traffic from local machine to remote container.
Prometheus and Grafana
Add the chart
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
You can search and verify the availability:
helm search repo prometheus-community
Install Helm chart:
helm install prometheus prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-statck
To install the Grafana:
helm install prometheus prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack
You can use the following command to get the port to access the Grafana:
kubectl describe pods prometheus-grafana-56f54d5c96-sj9vm
Port forward to access the Grafana from the master node (192.168.1.160):
kubectl port-forward prometheus-grafana-56f54d5c96-sj9vm 8080:3000
Use the following command to access the port via localhost:
ssh -L 8080:localhost:8080 oj@192.168.1.160
Now, you can access the Grafana via http://localhost:8080.
But you need user/password. Therefore, find the secrets to login to the Grafana:
kubectl get secret prometheus-grafana -o jsonpath='{.data}'
Use the following command to find the user/password:
echo <user/password> | base64 --decode
Dashboard
In the master, add the repository
helm repo add kubernetes-dashboard https://kubernetes.github.io/dashboard/
In the master, install
helm upgrade --install kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard/kubernetes-dashboard --create-namespace --namespace kubernetes-dashboard
Port forward in the master:
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard port-forward svc/kubernetes-dashboard-kong-proxy 8443:443
Create the fabric-rbac.yaml:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: fabric8-rbac
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
# Reference to upper's `metadata.name`
name: default
# Reference to upper's `metadata.namespace`
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
In the master, apply the following
kubectl apply -f fabric-rbac.yaml
NOTE: Please use the delete instead of apply if you want to delete.
In the master, create the token:
kubectl -n default create token default
This token is the bearer token, which you can use to log in to the dashboard.
References: