DevOps
- AWS DevOps
- HTTP
- Azure DevOps
- Docker Compose
- How to Download and Import Docker Images in WSL2
- Maven
Here the important commands and information collected while programming.
AWS DevOps
Caller Identity
echo $(aws sts get-caller-identity --query='Account' --output=text)
Command to get the token.
Cleaning resources
Only once you have to run the following:
aws resource-explorer-2 create-index --region us-east-1
To get all the resources:
aws resource-explorer-2 search --query-string "*"
To list the resources by Service:
aws resource-explorer-2 search --query-string "*" | jq '.Resources[] | select(.Service == "sagemaker") | {Region, OwningAccountId, ResourceType, Arn}'
For example, to delete the MLFlow resource
aws sagemaker delete-mlflow-tracking-server --tracking-server-name ojtrackingserver
To delete associations:
-
first list the association:
aws sagemaker list-associations \ --destination-arn "arn:aws:sagemaker:REGION:ACCOUNT:artifact/ARTIFACT_NAME" -
To delete the association:
# Delete association by ARN aws sagemaker delete-association \ --source-arn "arn:aws:sagemaker:region:account:artifact/artifact-name" \ --destination-arn "arn:aws:sagemaker:region:account:trial-component/component-name" -
Delete the artifact now:
aws sagemaker delete-artifact --artifact-arn \ "arn:aws:sagemaker:REGION:ACCOUNT:artifact/ARTIFACT_NAME"
Important commands
- List all unique services:
aws resource-explorer-2 search --query-string "*" | jq -r '.Resources[].Service' | sort -u
- Get a count of resources per service:
aws resource-explorer-2 search --query-string "*" | jq -r '.Resources[].Service' | sort | uniq -c | sort -rn - List services with sample resource types:
aws resource-explorer-2 search --query-string "*" | jq -r '.Resources[] | "\(.Service):\(.ResourceType)"' | sort -u - Get a structured summary by service:
aws resource-explorer-2 search --query-string "*" | jq 'group_by(.Resources[].Service) | map({service: .[0].Service, count: length})' - List all resources grouped by service: ```bash aws resource-explorer-2 search –query-string “*” | jq ‘.Resources | group_by(.Service) | map({Service: .[0].Service, Count: length, ResourceTypes:
[.[].ResourceType] | unique})’
### EC2
#### Dev environment Tools to install
Here the tool to install when you need EC2 instance as Dev
```yaml
UserData:
Fn::Base64: |
#!/bin/bash -xe
echo "Update..."
yum update -y
echo "Installing tmux..."
yum -y install tmux
echo "Installing development libs..."
yum -y install @development zlib-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel readline-devel sqlite sqlite-devel openssl-devel xz xz-devel libffi-devel findutils
echo "Installing git..."
yum -y install git
echo "Installing jq..."
yum -y install jq
echo "Installing docker..."
amazon-linux-extras install -y docker
echo "Add ec2-user to docker..."
usermod -a -G docker ec2-user
# # curl -LS --connect-timeout 15 \
# # --retry 5 \
# # --retry-delay 5 \
# # --retry-max-time 60 \
# # "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip"
# # unzip -u awscliv2.zip
# # ./aws/install
# # rm awscliv2.zip
wait
echo "Installing AWS SAM..."
curl -LS --connect-timeout 15 \
--retry 5 \
--retry-delay 5 \
--retry-max-time 60 \
"https://github.com/aws/aws-sam-cli/releases/latest/download/aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip"
unzip aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip -d sam-installation
./sam-installation/install
rm aws-sam-cli-linux-x86_64.zip
wait
sudo -u ec2-user -i <<'EOF'
echo '--- Install docker-compose for ec2-user ---'
echo 'export DOCKER_CONFIG=${DOCKER_CONFIG:-$HOME/.docker}' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'export PATH="$DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
mkdir -p $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins
curl -LS --connect-timeout 15 \
--retry 5 \
--retry-delay 0 \
--retry-max-time 60 \
https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/v2.11.0/docker-compose-linux-x86_64 -o $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins/docker-compose
chmod +x $DOCKER_CONFIG/cli-plugins/docker-compose
echo '--- Install pyenv for ec2-user ---'
source ~/.bashrc
RETRIES=3; DELAY=10; COUNT=1; while [ $COUNT -lt $RETRIES ]; do git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv.git $HOME/.pyenv; if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then RETRIES=0; break; fi; let COUNT=$COUNT+1; sleep $DELAY; done
echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="$HOME/.pyenv"' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'command -v pyenv >/dev/null || export PATH="$PYENV_ROOT/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
RETRIES=3; DELAY=10; COUNT=1; while [ $COUNT -lt $RETRIES ]; do git clone https://github.com/pyenv/pyenv-virtualenv.git $(pyenv root)/plugins/pyenv-virtualenv; if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then RETRIES=0; break; fi; let COUNT=$COUNT+1; sleep $DELAY; done
echo '--- Install git-remote for ec2-user ---'
pip3 install git-remote-codecommit
echo "Insalling python environment for AWS Lambda development..."
echo 'export TMPDIR="$HOME/tmp"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
RETRIES=3; DELAY=10; COUNT=1; while [ $COUNT -lt $RETRIES ]; do pyenv install 3.9.14 ; if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then RETRIES=0; break; fi; let COUNT=$COUNT+1; sleep $DELAY; done
pyenv virtualenv 3.9.14 p39
echo '--- end ---'
EOF
Execute AWS stepfunction:
jq -c . <input file>.json | xargs -0 aws stepfunctions start-execution --state-machine-arn <stepfunction arn>--input
EC2 Role for the VSCode
If your EC2 instance has been created in the private subnet, you have to create a role with the following policies:
NOTE: Trust relationship should be the EC2 and the developer should be with the PowerUserAccess.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"cloudformation:*",
"lambda:*",
"sns:*",
"events:*",
"logs:*",
"ec2:*",
"s3:*",
"dynamodb:*",
"kms:*",
"iam:*",
"states:*",
"sts:*",
"sqs:*",
"elasticfilesystem:*",
"config:*",
"cloudwatch:*",
"apigateway:*",
"backup:*",
"firehose:*",
"backup-storage:*",
"ssm:*"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Effect": "Allow"
}
]
}
and
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "CloudFormationTemplate",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudformation:CreateChangeSet"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:aws:transform/Serverless-2016-10-31"
]
},
{
"Sid": "CloudFormationStack",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"cloudformation:CreateChangeSet",
"cloudformation:CreateStack",
"cloudformation:DeleteStack",
"cloudformation:DescribeChangeSet",
"cloudformation:DescribeStackEvents",
"cloudformation:DescribeStacks",
"cloudformation:ExecuteChangeSet",
"cloudformation:GetTemplateSummary",
"cloudformation:ListStackResources",
"cloudformation:UpdateStack"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:cloudformation:*:<account id>:stack/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "S3",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:CreateBucket",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::*/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "ECRRepository",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability",
"ecr:BatchGetImage",
"ecr:CompleteLayerUpload",
"ecr:CreateRepository",
"ecr:DeleteRepository",
"ecr:DescribeImages",
"ecr:DescribeRepositories",
"ecr:GetDownloadUrlForLayer",
"ecr:GetRepositoryPolicy",
"ecr:InitiateLayerUpload",
"ecr:ListImages",
"ecr:PutImage",
"ecr:SetRepositoryPolicy",
"ecr:UploadLayerPart"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:ecr:*:<account id>:repository/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "ECRAuthToken",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"ecr:GetAuthorizationToken"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "Lambda",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"lambda:AddPermission",
"lambda:CreateFunction",
"lambda:DeleteFunction",
"lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:GetFunctionConfiguration",
"lambda:ListTags",
"lambda:RemovePermission",
"lambda:TagResource",
"lambda:UntagResource",
"lambda:UpdateFunctionCode",
"lambda:UpdateFunctionConfiguration"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:lambda:*:<account id>:function:*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "IAM",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"iam:CreateRole",
"iam:AttachRolePolicy",
"iam:DeleteRole",
"iam:DetachRolePolicy",
"iam:GetRole",
"iam:TagRole"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:iam::<account id>:role/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "IAMPassRole",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "iam:PassRole",
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"iam:PassedToService": "lambda.amazonaws.com"
}
}
},
{
"Sid": "APIGateway",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"apigateway:DELETE",
"apigateway:GET",
"apigateway:PATCH",
"apigateway:POST",
"apigateway:PUT"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:apigateway:*::*"
]
}
]
}
AWS KMS
#encrypt the password: InsightReadWrite
aws kms encrypt --key-id cfc7acf7-4f20-49c3-aa11-8be4cdc3291d --output text --query CiphertextBlob --plaintext InsightReadWrite
#encrypt the password: InsightReadWrite
aws kms encrypt --key-id cfc7acf7-4f20-49c3-aa11-8be4cdc3291d --plaintext fileb://test.txt --output text | base64 --decode > out.txt
#decrypt the password: InsightReadWrite
aws kms decrypt --ciphertext-blob fileb://out.txt --output text --query Plaintext | base64 --decode
AWS Athena JDBC
Here the the code to connect to the athena using JDBC:
from awsglue.context import GlueContext
# ...
# create Athena JDBC connection
con = (
glueContext.read.format("jdbc")
.option("driver", "com.simba.athena.jdbc.Driver")
.option("AwsCredentialsProviderClass","com.simba.athena.amazonaws.auth.InstanceProfileCredentialsProvider")
.option("url", "jdbc:awsathena://athena.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com:443")
.option("S3OutputLocation","s3://{}/temp/{}".format(args['<destination bucket>'], datetime.now().strftime("%m%d%y%H%M%S")))
)
Above code has been used in the Glue script.
AWS Cloudformation
Stack creation with IAM role
Here the role CF:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: create IAM role
Resources:
IamRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Sid: AllowAssumeRole
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service: "cloudformation.amazonaws.com"
Action: "sts:AssumeRole"
ManagedPolicyArns:
- "arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess"
Outputs:
IamRole:
Value: !GetAtt IamRole.Arn
Then create a stack from the file:
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name cfniamrole --capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM --template-body file://MyIamRole.yaml
Get the IAM Role ARN to the following variable IAM_ROLE_ARN
IAM_ROLE_ARN=$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name cfniamrole --query "Stacks[0].Outputs[?OutputKey=='IamRole'].OutputValue" --output text)
Example, here the stack for a S3 bucket:
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: "2010-09-09"
Description: This is my first bucket
Resources:
ojithadeletebucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
Create a bucket using IAM_ROLE_ARN role and the CF file.
aws cloudformation create-stack --stack-name mybucket --template-body file://mybucket.yaml --role-arn $IAM_ROLE_ARN
Delete the stack as this way:
for i in mybucket cfniamrole; do aws cloudformation delete-stack --stack-name $i;done
AWS EMR
command to create EMR cluster
aws emr create-cluster \
--name "OJCluster" \
--log-uri "s3n://<provide s3bucket prefix>-oj-temp/emr/logs/" \
--release-label "emr-6.3.1" \
--service-role "EMR_DefaultRole" \
--ec2-attributes '{"InstanceProfile":"EMR_EC2_DefaultRole","EmrManagedMasterSecurityGroup":"sg-<provide Master group id for Elastic MapReduce>","EmrManagedSlaveSecurityGroup":"sg-<provide Slave group id for Elastic MapReduce>","KeyName":"oj-public-key","AdditionalMasterSecurityGroups":[],"AdditionalSlaveSecurityGroups":[],"ServiceAccessSecurityGroup":"sg-<provide Service access group id for Elastic MapReduce>","SubnetId":"subnet-<provide subnet-id>"}' \
--applications Name=Hadoop Name=JupyterEnterpriseGateway Name=Spark Name=Ganglia Name=Zeppelin Name=Livy \
--configurations '[{"Classification":"spark-hive-site","Properties":{"hive.metastore.client.factory.class":"com.amazonaws.glue.catalog.metastore.AWSGlueDataCatalogHiveClientFactory"}}]' \
--instance-groups '[{"InstanceCount":1,"InstanceGroupType":"MASTER","Name":"Master - 1","InstanceType":"m5.xlarge","EbsConfiguration":{"EbsBlockDeviceConfigs":[{"VolumeSpecification":{"VolumeType":"gp2","SizeInGB":32},"VolumesPerInstance":2}]}},{"InstanceCount":1,"InstanceGroupType":"CORE","Name":"Core - 2","InstanceType":"m5.xlarge","EbsConfiguration":{"EbsBlockDeviceConfigs":[{"VolumeSpecification":{"VolumeType":"gp2","SizeInGB":32},"VolumesPerInstance":2}]}}]' \
--auto-scaling-role "EMR_AutoScaling_DefaultRole" \
--scale-down-behavior "TERMINATE_AT_TASK_COMPLETION" \
--ebs-root-volume-size "10" \
--region "ap-southeast-2"
EMRClusterID=$(aws emr list-clusters | jq '.Clusters[0].Id' | tr -d '"') && echo $EMRClusterID
review host
HOST=$(aws emr describe-cluster --cluster-id $EMRClusterID | jq '.Cluster.MasterPublicDnsName' | tr -d '"') && echo $HOST
To connect to the EMR cluster, run:
sudo ssh -i /home/ec2-user/<emr key>.pem hadoop@$HOST
Set the lab data bucket
LABDATABUCKET=$(aws s3api list-buckets --query "Buckets[?starts_with(Name, 'lab-data-')].Name" --output text)
echo $LABDATABUCKET
submit job
aws emr add-steps \
--cluster-id $EMRClusterID \
--steps Type=Spark,Name="MySparkApplication",ActionOnFailure=CONTINUE,Args=[s3://$LABDATABUCKET/iris_data.py,--data_source,s3://$LABDATABUCKET/iris_data.csv,--output_uri,s3://$LABDATABUCKET/output]
To check
aws emr describe-step --cluster-id $EMRClusterID --step-id <step id>
sample output of above is
{
"Step": {
"Id": "<step id>",
"Name": "MySparkApplication",
"Config": {
"Jar": "command-runner.jar",
"Properties": {},
"Args": [
"spark-submit",
"s3://data-bucket-d47a5bd0/iris_data.py",
"--data_source",
"s3://data-bucket-d47a5bd0/iris_data.csv",
"--output_uri",
"s3://data-bucket-d47a5bd0/output"
]
},
"ActionOnFailure": "CONTINUE",
"Status": {
"State": "COMPLETED",
"StateChangeReason": {},
"Timeline": {
"CreationDateTime": "2025-08-04T12:04:23.646000+00:00",
"StartDateTime": "2025-08-04T12:04:39.955000+00:00",
"EndDateTime": "2025-08-04T12:05:44.485000+00:00"
}
}
}
}
To terminate cluster
aws emr terminate-clusters --cluster-ids $EMRClusterID
AWS Chalice
Package first :
aws cloudformation package --template-file out/sam.json --s3-bucket ojemr --output-template-file pkg.yaml
Deploy :
aws cloudformation deploy --template-file /home/cloudera/dev/hellochalice/pkg.yaml --stack-name hellochalice --capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM
SQL Server
Login to the docker:
docker exec -i -t 8ae7c51a90fe /bin/bash
Create a new folder in the /var/opt/mssql
cd /var/opt/mssql/
mkdir backup
Download the AdventureWork from https://msftdbprodsamples.codeplex.com/downloads/get/880661 to your local machine and unzip.
docker cp AdventureWorks2014.bak 8ae7c51a90fe:/var/opt/mssql/backup
In your host machine use the sqlcmd
sqlcmd -S 127.0.0.1 -U SA -P '<password>'
Following the link https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/linux/sql-server-linux-migrate-restore-database
Restore the backup file:
RESTORE DATABASE AdventureWorks
FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/AdventureWorks2014.bak'
WITH MOVE 'AdventureWorks2014_Data' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/AdventureWorks2014_Data.mdf',
MOVE 'AdventureWorks2014_Log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/AdventureWorks2014_Log.ldf'
GO
How to start docker again
#find the container id
docker ps -a
#start that container id
docker start <container-id>
Dynamodb
List all the tables
aws dynamodb list-tables
describe a table found in the above command:
aws dynamodb describe-table --table-name <table name>
HTTP
Status Codes
- 1nn: informational
- 2nn: success
- 3nn: redirection
- 4nn: client errors
- 5nn: server errors
200 common
- 200 ok: everything ok
- 201 created: Returns a location header for new resources
- 202 Accepted: Server has accepted the request, but it is not yet complete.
400 common
- 400 Bad Request: Malformed Syntax, retry with change
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication is required
- 403 Forbidded: Server has understood, but refuses request
- 404 Not Found: Server can’t find a resource for URI
- 406 Incompatible: Incompatible Accept headers specified
- 409 Conflict: Resource conflicts with client request
Azure DevOps
List the regions
az account list-locations --query "[].{Name: name, DisplayName: displayName}" --output table
Set the default region to Sydney
az configure --defaults location=australiaeast
In the cloudeshell created random number generator
resourceSuffix=$RANDOM
Azure Simple pipeline with stages
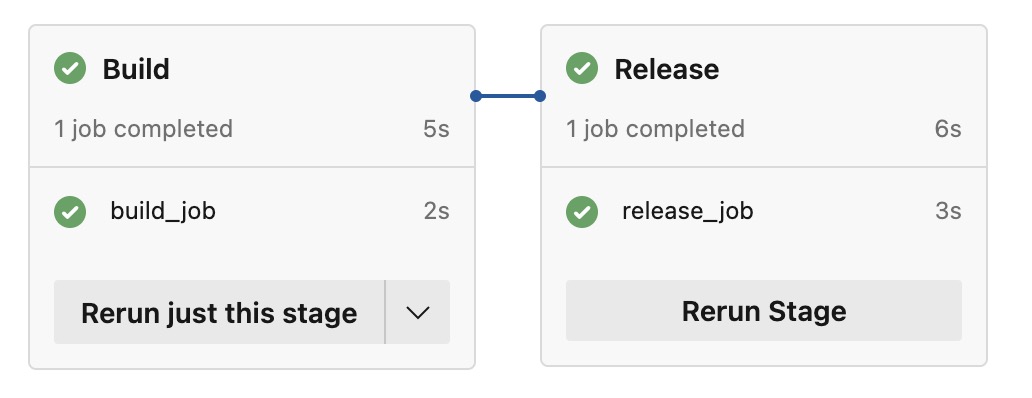
Here the code for the above Build and release pipeline
trigger:
- azure-pipelines
pool:
vmImage: ubuntu-latest
stages:
- stage: Build
jobs:
- job: build_job
steps:
- bash: echo 'Build stage job.'
displayName: 'Run a one-line script'
- stage: Release
jobs:
- job: release_job
steps:
- bash: echo 'Relase stage job'
displayName: 'Run a one-line script'
To run the pipeline on CRON1:
schedules:
- cron: '0 0 * * *'
displayName: Daily midnight build
branches:
include:
- main
To force a pipeline to run even when there are no code changes, you can use the always keyword.
schedules:
- cron: ...
...
always: true
For the following
Every Monday - Friday at 3:00 AM (UTC + 5:30 time zone), build branches that meet the features/india/* branch filter criteria

schedules:
- cron: '30 21 * * Sun-Thu'
displayName: M-F 3:00 AM (UTC + 5:30) India daily build
branches:
include:
- /features/india/*
The cron syntax (mm HH DD MM DW) is 30 21 * * Sun-Thu. Minutes and Hours - 30 21 - This maps to 21:30 UTC (9:30 PM UTC). Since the specified time zone in the classic editor is UTC + 5:30, we need to subtract 5 hours and 30 minutes from the desired build time of 3:00 AM to arrive at the desired UTC time to specify for the YAML trigger.
Days of the week -
Sun-Thu- because of the timezone conversion, for our builds to run at 3:00 AM in the UTC + 5:30 India time zone, we need to specify starting them the previous day in UTC time. We could also specify the days of the week as0-4or0,1,2,3,4.
Every Monday - Friday at 3:00 AM (UTC - 5:00 time zone), build branches that meet the features/nc/* branch filter criteria
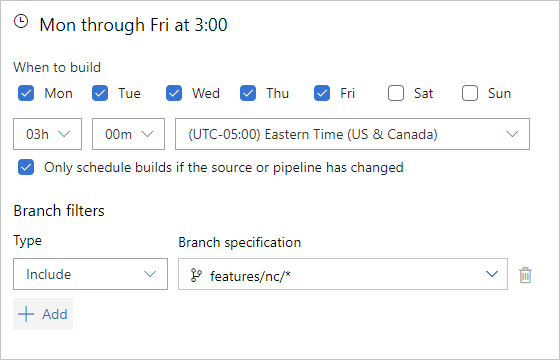
The CRON is
...
- cron: '0 8 * * Mon-Fri'
displayName: M-F 3:00 AM (UTC - 5) NC daily build
branches:
include:
- /features/nc/*
Azure Docker build pipeline
Here the folder structure
.
├── Dockerfile
├── README.md
└── azure-pipelines.yml
Sample Dockerfile
FROM bitnami/minideb:latest
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
build pipeline:
# Docker
# Build a Docker image and save it as a tar file
# https://docs.microsoft.com/azure/devops/pipelines/languages/docker
trigger:
- master
resources:
- repo: self
variables:
# tag: '$(Build.BuildId)'
tag: 'latest'
DOCKER_BUILDKIT: 1
imageName: 'ojitha/test'
# Create a simpler output filename without the repository path structure
imageFileName: 'test-$(tag).tar'
stages:
- stage: Build
displayName: Build image
jobs:
- job: Build
displayName: Build
pool:
name: Ubuntu
demands:
- agent.name -equals ojitha
steps:
- task: Docker@2
displayName: Build an image
inputs:
repository: $(imageName)
command: build
dockerfile: '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/Dockerfile'
tags: |
$(tag)
- script: |
# Create the directory if it doesn't exist
mkdir -p $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)
# Save the Docker image to a tar file with a simpler name
docker save $(imageName):$(tag) -o $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)/$(imageFileName)
# Display saved file for verification
ls -la $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)
displayName: 'Save Docker image to tar file'
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
inputs:
pathToPublish: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
artifactName: 'docker-image'
displayName: 'Publish Docker image tar file as artifact'
Azure pipeline to save the Docker images to pipeline artifacts
You can save the docker generated artifacts as follows:
Here the azure-pipelines.yml:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
variables:
# Docker image configuration
imageName: 'myapp'
imageTag: '$(Build.BuildNumber)'
dockerfilePath: '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)/app/Dockerfile'
# Artifact configuration
artifactName: 'docker-images'
dockerTarFileName: '$(imageName)-$(imageTag).tar'
stages:
- stage: BuildDockerImage
displayName: 'Build Docker Image'
jobs:
- job: BuildAndSaveImage
displayName: 'Build and Save Docker Image'
steps:
# Checkout source code
- checkout: self
displayName: 'Checkout source code'
# Display environment info
- script: |
echo "Pipeline: $(Build.DefinitionName)"
echo "Build Number: $(Build.BuildNumber)"
echo "Source Branch: $(Build.SourceBranchName)"
echo "Docker Image: $(imageName):$(imageTag)"
echo "Dockerfile Path: $(dockerfilePath)"
docker --version
df -h
displayName: 'Display build information'
# Build Docker image
- script: |
echo "Building Docker image: $(imageName):$(imageTag)"
docker build -t $(imageName):$(imageTag) -f $(dockerfilePath) .
# Also tag as latest for convenience
docker tag $(imageName):$(imageTag) $(imageName):latest
# Display images
docker images | grep $(imageName)
displayName: 'Build Docker image'
workingDirectory: '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)'
# Optional: Test the Docker image
- script: |
echo "Testing Docker image..."
# Run basic container test
docker run --rm $(imageName):$(imageTag) --version || true
# Check image size
docker images $(imageName):$(imageTag) --format "table {{.Repository}}\t{{.Tag}}\t{{.Size}}"
displayName: 'Test Docker image'
condition: succeeded()
# Save Docker image to tar file
- script: |
echo "Saving Docker image to tar file..."
mkdir -p $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts
# Save both tagged version and latest
docker save $(imageName):$(imageTag) $(imageName):latest -o $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/$(dockerTarFileName)
# Display file info
ls -lh $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/
echo "Docker image saved as: $(dockerTarFileName)"
echo "File size: $(du -h $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/$(dockerTarFileName) | cut -f1)"
displayName: 'Save Docker image to tar file'
# Create metadata file
- script: |
echo "Creating metadata file..."
cat > $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/image-info.txt << EOF
Docker Image Information
========================
Image Name: $(imageName)
Image Tag: $(imageTag)
Build Number: $(Build.BuildNumber)
Build Date: $(date)
Source Branch: $(Build.SourceBranchName)
Commit ID: $(Build.SourceVersion)
Pipeline: $(Build.DefinitionName)
Tar File: $(dockerTarFileName)
Import Instructions:
===================
1. Download the artifact from Azure DevOps
2. Extract the tar file
3. Load into Docker: docker load -i $(dockerTarFileName)
4. Verify: docker images | grep $(imageName)
5. Run: docker run --rm $(imageName):$(imageTag)
EOF
cat $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/image-info.txt
displayName: 'Create metadata file'
# Optional: Create compressed version to save space
- script: |
echo "Creating compressed version..."
cd $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts
# Compress the tar file
gzip -c $(dockerTarFileName) > $(dockerTarFileName).gz
# Display sizes
echo "Original size: $(du -h $(dockerTarFileName) | cut -f1)"
echo "Compressed size: $(du -h $(dockerTarFileName).gz | cut -f1)"
# Keep both versions
ls -lh
displayName: 'Create compressed version'
condition: succeeded()
# Publish Docker image as pipeline artifact
- task: PublishPipelineArtifact@1
inputs:
targetPath: '$(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts'
artifactName: '$(artifactName)'
publishLocation: 'pipeline'
displayName: 'Publish Docker image artifact'
# Clean up local Docker images to save space
- script: |
echo "Cleaning up local Docker images..."
docker rmi $(imageName):$(imageTag) $(imageName):latest || true
docker system prune -f
df -h
displayName: 'Clean up Docker images'
condition: always()
# Optional: Additional stage for multi-architecture builds
- stage: BuildMultiArch
displayName: 'Build Multi-Architecture Images'
condition: and(succeeded(), eq(variables['Build.SourceBranchName'], 'main'))
dependsOn: []
jobs:
- job: BuildMultiArchImage
displayName: 'Build Multi-Arch Docker Image'
steps:
- checkout: self
# Set up Docker Buildx for multi-platform builds
- script: |
# Enable experimental features
echo '{"experimental": true}' | sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json
sudo systemctl restart docker
# Set up buildx
docker buildx create --name multiarch --use
docker buildx inspect --bootstrap
displayName: 'Setup Docker Buildx'
# Build multi-architecture images
- script: |
echo "Building multi-architecture Docker images..."
# Build for multiple platforms
docker buildx build \
--platform linux/amd64,linux/arm64 \
--tag $(imageName):$(imageTag)-multiarch \
--file $(dockerfilePath) \
--output type=docker,dest=$(Agent.TempDirectory)/$(imageName)-$(imageTag)-multiarch.tar \
.
ls -lh $(Agent.TempDirectory)/$(imageName)-$(imageTag)-multiarch.tar
displayName: 'Build multi-architecture image'
workingDirectory: '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)'
# Publish multi-arch artifact
- task: PublishPipelineArtifact@1
inputs:
targetPath: '$(Agent.TempDirectory)/$(imageName)-$(imageTag)-multiarch.tar'
artifactName: 'docker-images-multiarch'
publishLocation: 'pipeline'
displayName: 'Publish multi-arch Docker artifact'
Template for Dockerfiles
azure-pipelines.yml:
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
- master
variables:
# Global build configuration
buildNumber: '$(Build.BuildNumber)'
sourceBranch: '$(Build.SourceBranchName)'
# Build Docker images using the template
stages:
- stage: BuildDockerImages
displayName: 'Build Docker Images'
jobs:
# Build the main application Docker image
- template: templates/docker-build-template.yml
parameters:
imageName: 'myapp'
imageTag: '$(buildNumber)'
dockerfilePath: 'app/Dockerfile'
buildContext: '.'
artifactName: 'docker-images'
enableCompression: true
runTests: true
testCommand: '--version' # or 'none' to skip container testing
# Example: Build additional Docker image (uncomment and modify as needed)
# - template: templates/docker-build-template.yml
# parameters:
# imageName: 'myapp-worker'
# imageTag: '$(buildNumber)'
# dockerfilePath: 'worker/Dockerfile'
# buildContext: '.'
# artifactName: 'docker-images'
# enableCompression: true
# runTests: true
# testCommand: '--help'
# Example: Build a different component with custom build args
# - template: templates/docker-build-template.yml
# parameters:
# imageName: 'myapp-api'
# imageTag: '$(buildNumber)'
# dockerfilePath: 'api/Dockerfile'
# buildContext: 'api'
# buildArgs: 'NODE_ENV=production API_VERSION=v2'
# artifactName: 'docker-images'
# enableCompression: true
# runTests: true
# testCommand: 'node --version'
# Optional: Deployment stage that depends on all build stages
- stage: PostBuild
displayName: 'Post-Build Activities'
dependsOn:
- BuildDockerImages
condition: succeeded()
jobs:
- job: PostBuildTasks
displayName: 'Post-Build Tasks'
steps:
# Display build summary
- script: |
echo "========================================"
echo "Build Summary"
echo "========================================"
echo "Build completed successfully!"
echo "Build Number: $(buildNumber)"
echo "Source Branch: $(sourceBranch)"
echo "Commit: $(Build.SourceVersion)"
echo ""
echo "Images built:"
echo "- myapp:$(buildNumber)"
echo ""
echo "Artifacts available:"
echo "- docker-images-myapp"
echo ""
echo "Next steps:"
echo "1. Download artifacts from this build"
echo "2. Load Docker images: docker load -i <tar-file>"
echo "3. Deploy to target environment"
echo "========================================"
displayName: 'Build Summary'
# Optional: Send notification or trigger deployment pipeline
# Add your post-build tasks here
# Optional: Example of conditional builds based on changed files
# This stage only runs if files in the 'app' directory changed
- stage: BuildOnAppChanges
displayName: 'Build App (Only on Changes)'
condition: |
and(
succeeded(),
or(
contains(variables['Build.SourceVersionMessage'], 'app/'),
eq(variables['Build.Reason'], 'Manual')
)
)
dependsOn: []
jobs:
- template: templates/docker-build-template.yml
parameters:
imageName: 'myapp-changed'
imageTag: '$(buildNumber)-hotfix'
dockerfilePath: 'Dockerfile'
buildContext: '.'
artifactName: 'hotfix-images'
enableCompression: true
runTests: true
templates/docker-build-template.yml:
parameters:
# Required parameters
- name: imageName
type: string
displayName: 'Docker image name'
- name: dockerfilePath
type: string
displayName: 'Path to Dockerfile relative to repository root'
# Optional parameters with defaults
- name: imageTag
type: string
displayName: 'Docker image tag'
default: '$(Build.BuildNumber)'
- name: buildContext
type: string
displayName: 'Docker build context path'
default: '$(Build.SourcesDirectory)'
- name: buildArgs
type: string
displayName: 'Docker build arguments (space-separated)'
default: ''
- name: artifactName
type: string
displayName: 'Pipeline artifact name'
default: 'docker-images'
- name: enableCompression
type: boolean
displayName: 'Enable gzip compression of tar file'
default: true
- name: runTests
type: boolean
displayName: 'Run basic container tests'
default: true
- name: testCommand
type: string
displayName: 'Command to test the container (optional)'
default: '--version'
jobs:
- job: BuildDockerImage
displayName: 'Build Docker Image'
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
variables:
dockerTarFileName: '${{ parameters.imageName }}-${{ parameters.imageTag }}.tar'
fullImageName: '${{ parameters.imageName }}:${{ parameters.imageTag }}'
steps:
- checkout: self
displayName: 'Checkout source code'
- script: |
set -e
echo "========================================"
echo "Docker Build Information"
echo "========================================"
echo "Pipeline: $(Build.DefinitionName)"
echo "Build Number: $(Build.BuildNumber)"
echo "Source Branch: $(Build.SourceBranchName)"
echo "Commit ID: $(Build.SourceVersion)"
echo ""
echo "Docker Configuration:"
echo "- Image Name: ${{ parameters.imageName }}"
echo "- Image Tag: ${{ parameters.imageTag }}"
echo "- Full Image: $(fullImageName)"
echo "- Dockerfile Path: ${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}"
echo "- Build Context: ${{ parameters.buildContext }}"
echo "- Build Args: ${{ parameters.buildArgs }}"
echo ""
echo "Build Options:"
echo "- Run Tests: ${{ parameters.runTests }}"
echo "- Enable Compression: ${{ parameters.enableCompression }}"
echo ""
echo "System Information:"
docker --version
echo "Available disk space:"
df -h
echo "========================================"
displayName: 'Display build information'
# Validate Dockerfile exists
- script: |
set -e
if [ ! -f "${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}" ]; then
echo "Error: Dockerfile not found at ${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}"
exit 1
fi
echo "✓ Dockerfile found at ${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}"
# Show Dockerfile contents (first 20 lines)
echo ""
echo "Dockerfile preview:"
echo "==================="
head -20 "${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}"
echo "==================="
displayName: 'Validate Dockerfile'
# Build Docker image
- script: |
set -e
echo "Building Docker image: $(fullImageName)"
echo "Context: ${{ parameters.buildContext }}"
# Prepare build command
BUILD_CMD="docker build -t $(fullImageName) -f ${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}"
# Add build args if provided
if [ -n "${{ parameters.buildArgs }}" ]; then
for arg in ${{ parameters.buildArgs }}; do
BUILD_CMD="$BUILD_CMD --build-arg $arg"
done
echo "Build arguments: ${{ parameters.buildArgs }}"
fi
# Add build context
BUILD_CMD="$BUILD_CMD ${{ parameters.buildContext }}"
echo "Executing: $BUILD_CMD"
eval $BUILD_CMD
# Also tag as latest for convenience
docker tag $(fullImageName) ${{ parameters.imageName }}:latest
# Display built images
echo ""
echo "Built images:"
docker images | grep ${{ parameters.imageName }}
displayName: 'Build Docker image'
# Test the Docker image (if enabled)
- script: |
set -e
echo "Testing Docker image: $(fullImageName)"
# Basic image inspection
echo "Image details:"
docker inspect $(fullImageName) --format='{{.Config.ExposedPorts}}'
docker inspect $(fullImageName) --format='{{.Config.Env}}'
# Run test command if provided
if [ -n "${{ parameters.testCommand }}" ] && [ "${{ parameters.testCommand }}" != "none" ]; then
echo "Running test command: ${{ parameters.testCommand }}"
docker run --rm $(fullImageName) ${{ parameters.testCommand }} || {
echo "Test command failed, but continuing build..."
}
fi
# Check image size
echo ""
echo "Image size information:"
docker images $(fullImageName) --format "table {{.Repository}}\t{{.Tag}}\t{{.Size}}\t{{.CreatedAt}}"
# Check for security issues (basic)
echo ""
echo "Basic security check:"
docker run --rm $(fullImageName) whoami 2>/dev/null || echo "Cannot check user (expected for some images)"
displayName: 'Test Docker image'
condition: eq(${{ parameters.runTests }}, true)
# Save Docker image to tar file
- script: |
set -e
echo "Saving Docker image to tar file..."
mkdir -p $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts
# Save both tagged version and latest
echo "Saving images: $(fullImageName) and ${{ parameters.imageName }}:latest"
docker save $(fullImageName) ${{ parameters.imageName }}:latest -o $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/$(dockerTarFileName)
# Display file info
echo ""
echo "Artifact created:"
ls -lh $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/
echo "Docker image saved as: $(dockerTarFileName)"
file_size=$(du -h $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/$(dockerTarFileName) | cut -f1)
echo "File size: $file_size"
# Store file size for use in metadata
echo "##vso[task.setvariable variable=dockerTarFileSize]$file_size"
displayName: 'Save Docker image to tar file'
# Create compressed version (if enabled)
- script: |
set -e
echo "Creating compressed version..."
cd $(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts
# Compress the tar file
echo "Compressing $(dockerTarFileName)..."
gzip -c $(dockerTarFileName) > $(dockerTarFileName).gz
# Display sizes (use stat -c on Linux instead of -f)
original_size=$(stat -c%s $(dockerTarFileName))
compressed_size=$(stat -c%s $(dockerTarFileName).gz)
echo "Compression results:"
echo "- Original size: $(du -h $(dockerTarFileName) | cut -f1)"
echo "- Compressed size: $(du -h $(dockerTarFileName).gz | cut -f1)"
# Calculate compression ratio
ratio=$(echo "scale=1; $compressed_size * 100 / $original_size" | bc -l)
echo "- Compression ratio: ${ratio}%"
echo ""
echo "All artifacts:"
ls -lh
displayName: 'Create compressed version'
condition: eq(${{ parameters.enableCompression }}, true)
# Create metadata file
- script: |
set -e
echo "Creating metadata file..."
metadata_file="$(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts/image-info.txt"
cat > "$metadata_file" << EOF
Docker Image Build Information
==============================
Build Details:
--------------
Image Name: ${{ parameters.imageName }}
Image Tag: ${{ parameters.imageTag }}
Full Image: $(fullImageName)
Build Number: $(Build.BuildNumber)
Build Date: $(date -u '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S UTC')
Source Branch: $(Build.SourceBranchName)
Commit ID: $(Build.SourceVersion)
Pipeline: $(Build.DefinitionName)
Configuration:
--------------
Dockerfile Path: ${{ parameters.dockerfilePath }}
Build Context: ${{ parameters.buildContext }}
Build Args: ${{ parameters.buildArgs }}
Artifact Details:
-----------------
Tar File: $(dockerTarFileName)
File Size: $(dockerTarFileSize)
Compressed: ${{ parameters.enableCompression }}
Usage Instructions:
===================
1. Download the artifact from Azure DevOps
2. Extract the tar file from the artifact zip
3. Load into Docker:
docker load -i $(dockerTarFileName)
4. Verify images:
docker images | grep ${{ parameters.imageName }}
5. Run container:
docker run --rm $(fullImageName)
Available tags after import:
- $(fullImageName)
- ${{ parameters.imageName }}:latest
EOF
echo "Metadata file created:"
cat "$metadata_file"
displayName: 'Create metadata file'
# Publish Docker image as pipeline artifact
- task: PublishPipelineArtifact@1
inputs:
targetPath: '$(Agent.TempDirectory)/docker-artifacts'
artifactName: '${{ parameters.artifactName }}-${{ parameters.imageName }}'
publishLocation: 'pipeline'
displayName: 'Publish Docker image artifact'
# Clean up local Docker images to save space
- script: |
set -e
echo "Cleaning up local Docker images..."
docker rmi $(fullImageName) ${{ parameters.imageName }}:latest || true
# Clean up any dangling images
docker system prune -f
echo "Remaining disk space:"
df -h
displayName: 'Clean up Docker images'
condition: always()
Enable logs in the Azure DevOps pipeline
Add the following steps to the pipeline
steps:
# Step 1: SSH to remote server and extract nginx logs to a file
- task: SSH@0
displayName: 'Extract Nginx Logs to File'
inputs:
sshEndpoint: 'MySSHConnection'
runOptions: 'inline'
inline: |
cd /path/to/your/compose/directory
# Create logs directory if it doesn't exist
mkdir -p /tmp/pipeline-logs
# Extract nginx logs with timestamp
echo "=== Nginx Logs - $(date) ===" > /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
podman-compose logs nginx --tail=1000 >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
# Extract error logs separately
echo "" >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
echo "=== Nginx Error Logs ===" >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
podman-compose logs nginx 2>&1 | grep -i error >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt || echo "No errors found" >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
# Container status for context
echo "" >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
echo "=== Container Status ===" >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
podman-compose ps >> /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt
# Show file was created
ls -la /tmp/pipeline-logs/
echo "Log file size: $(wc -l < /tmp/pipeline-logs/nginx-logs.txt) lines"
# Step 2: Copy the log file from remote server to pipeline agent
- task: CopyFilesOverSSH@0
displayName: 'Download Nginx Logs from Remote Server'
inputs:
sshEndpoint: 'MySSHConnection'
sourceFolder: '/tmp/pipeline-logs'
contents: '*.txt'
targetFolder: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/nginx-logs'
isDownloadFiles: true # This is key - it downloads FROM the remote server
cleanTargetFolder: true
# Step 3: Publish logs as pipeline artifact
- task: PublishPipelineArtifact@1
displayName: 'Publish Nginx Logs as Artifact'
inputs:
targetPath: '$(Pipeline.Workspace)/nginx-logs'
artifact: 'nginx-logs'
publishLocation: 'pipeline'
condition: always() # Publish even if previous steps failed
Docker Compose
mkdir azagent;cd azagent;curl -fkSL -o vstsagent.tar.gz https://download.agent.dev.azure.com/agent/4.255.0/vsts-agent-linux-x64-4.255.0.tar.gz;tar -zxvf vstsagent.tar.gz; if [ -x "$(command -v systemctl)" ]; then ./config.sh --environment --environmentname "elasticsearch-production" --acceptteeeula --agent $HOSTNAME --url https://dev.azure.com/ojitha/ --work _work --projectname 'KibanaDockerCompose' --auth PAT --token <mytoken> --runasservice; sudo ./svc.sh install; sudo ./svc.sh start; else ./config.sh --environment --environmentname "elasticsearch-production" --acceptteeeula --agent $HOSTNAME --url https://dev.azure.com/ojitha/ --work _work --projectname 'KibanaDockerCompose' --auth PAT --token <mytoken>; ./run.sh; fi
How to Download and Import Docker Images in WSL2
Step 1: Download Artifacts from Azure DevOps
Method A: Using Azure DevOps Web Interface
- Navigate to your Azure DevOps project
- Go to Pipelines → Runs
- Click on the specific pipeline run
- Navigate to the Summary tab
- Scroll down to find Related section
- Click on Artifacts → docker-images
- Click Download to download the zip file
Method B: Using Azure CLI
# Install Azure CLI if not already installed
curl -sL https://aka.ms/InstallAzureCLIDeb | sudo bash
# Login to Azure
az login
# Set defaults
az devops configure --defaults organization=https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORG project=YOUR_PROJECT
# Download artifacts
az pipelines runs artifact download \
--artifact-name "docker-images" \
--path "./docker-artifacts" \
--run-id "BUILD_ID"
Method C: Using REST API
# Get the artifact download URL
curl -u "username:PAT_TOKEN" \
"https://dev.azure.com/YOUR_ORG/YOUR_PROJECT/_apis/build/builds/BUILD_ID/artifacts?artifactName=docker-images&api-version=6.0"
# Download the artifact
wget -O docker-images.zip "DOWNLOAD_URL_FROM_ABOVE"
Step 2: Prepare WSL2 Environment
Ensure Docker is Installed in WSL2
# Update Ubuntu
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
# Install Docker
sudo apt install -y docker.io
# Add user to docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
# Start Docker service
sudo service docker start
# Enable Docker to start automatically
sudo systemctl enable docker
# Verify Docker installation
docker --version
docker info
Alternative: Install Docker Desktop for Windows
- Docker Desktop automatically integrates with WSL2
- Provides better performance and resource management
Step 3: Extract and Import Docker Images
Extract Downloaded Artifacts
# Navigate to downloads directory
cd ~/Downloads
# Extract the artifact zip file
unzip docker-images.zip -d ./docker-artifacts
# Navigate to extracted directory
cd docker-artifacts
# List contents
ls -la
Import Docker Images
# Method 1: Import regular tar file
docker load -i myapp-123.tar
# Method 2: Import compressed tar file
gunzip -c myapp-123.tar.gz | docker load
# Method 3: Import with verbose output
docker load --input myapp-123.tar
# Verify imported images
docker images | grep myapp
Example Import Script
#!/bin/bash
# Script to import Docker images from Azure Pipeline artifacts
ARTIFACT_DIR="./docker-artifacts"
LOG_FILE="import.log"
echo "Starting Docker image import..." | tee $LOG_FILE
echo "Date: $(date)" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
# Check if Docker is running
if ! docker info >/dev/null 2>&1; then
echo "Docker is not running. Starting Docker..." | tee -a $LOG_FILE
sudo service docker start
sleep 5
fi
# Import all tar files in the directory
for tar_file in $ARTIFACT_DIR/*.tar; do
if [ -f "$tar_file" ]; then
echo "Importing: $tar_file" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
docker load -i "$tar_file" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
echo "Import completed for: $tar_file" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
fi
done
# Import compressed tar files
for tar_gz_file in $ARTIFACT_DIR/*.tar.gz; do
if [ -f "$tar_gz_file" ]; then
echo "Importing compressed: $tar_gz_file" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
gunzip -c "$tar_gz_file" | docker load | tee -a $LOG_FILE
echo "Import completed for: $tar_gz_file" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
fi
done
# Display imported images
echo "=== Imported Images ===" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
docker images | tee -a $LOG_FILE
echo "Import process completed!" | tee -a $LOG_FILE
Step 4: Verify and Test Imported Images
List All Images
# List all Docker images
docker images
# Filter by image name
docker images myapp
# Show image details
docker inspect myapp:latest
Test the Imported Image
# Run the container
docker run --rm -p 3000:3000 myapp:latest
# Run in detached mode
docker run -d --name myapp-test -p 3000:3000 myapp:latest
# Check container logs
docker logs myapp-test
# Stop and remove container
docker stop myapp-test
docker rm myapp-test
Run with Custom Configuration
# Run with environment variables
docker run --rm \
-e NODE_ENV=production \
-e PORT=8080 \
-p 8080:8080 \
myapp:latest
# Run with volume mapping
docker run --rm \
-v $(pwd)/data:/app/data \
-p 3000:3000 \
myapp:latest
# Run interactively
docker run --rm -it myapp:latest /bin/sh
Step 5: Automate the Process
PowerShell Script for Windows
# PowerShell script to download and import Docker images
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$BuildId,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$Organization,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$Project,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]$PAT
)
# Set up variables
$artifactName = "docker-images"
$downloadPath = "$env:TEMP\docker-artifacts"
# Create download directory
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Force -Path $downloadPath
# Download artifact using REST API
$headers = @{
Authorization = "Basic " + [Convert]::ToBase64String([Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes(":$PAT"))
}
$uri = "https://dev.azure.com/$Organization/$Project/_apis/build/builds/$BuildId/artifacts?artifactName=$artifactName&api-version=6.0"
$artifact = Invoke-RestMethod -Uri $uri -Headers $headers
# Download and extract
$downloadUrl = $artifact.resource.downloadUrl
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $downloadUrl -Headers $headers -OutFile "$downloadPath\artifacts.zip"
Expand-Archive -Path "$downloadPath\artifacts.zip" -DestinationPath $downloadPath -Force
# Import to WSL2
Write-Host "Importing to WSL2..."
wsl -d Ubuntu -e bash -c "cd /mnt/c/Users/$env:USERNAME/AppData/Local/Temp/docker-artifacts && docker load -i *.tar"
Write-Host "Import completed!"
Bash Script for Automated Download and Import
#!/bin/bash
# Configuration
ORG="your-organization"
PROJECT="your-project"
PAT="your-personal-access-token"
BUILD_ID="$1"
if [ -z "$BUILD_ID" ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <build-id>"
exit 1
fi
# Download artifact
echo "Downloading artifacts for build: $BUILD_ID"
curl -u ":$PAT" \
"https://dev.azure.com/$ORG/$PROJECT/_apis/build/builds/$BUILD_ID/artifacts?artifactName=docker-images&\$format=zip" \
-o docker-images.zip
# Extract
unzip docker-images.zip -d ./docker-artifacts
# Import
cd docker-artifacts
for tar_file in *.tar; do
if [ -f "$tar_file" ]; then
echo "Importing: $tar_file"
docker load -i "$tar_file"
fi
done
# Clean up
cd ..
rm -f docker-images.zip
rm -rf docker-artifacts
echo "Docker images imported successfully!"
docker images
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
- Docker not running in WSL2
sudo service docker start # Or enable systemd in WSL2 - Permission denied errors
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER # Logout and login again - Out of disk space
# Clean up Docker docker system prune -a # Check disk usage df -h - Import fails with “no space left on device”
# Increase WSL2 memory limit in .wslconfig echo -e "[wsl2]\nmemory=8GB\nswap=2GB" > ~/.wslconfig - Image not found after import
# Check if import was successful docker images # Re-import with verbose output docker load -i image.tar --quiet=false
Performance Optimization
Reduce Image Size
- Use compressed artifacts (tar.gz)
- Use multi-stage builds in Dockerfile
- Remove unnecessary files before creating image
Speed Up Transfer
- Use Azure Storage for large artifacts
- Implement incremental builds
- Cache base images locally
WSL2 Optimization
# Optimize WSL2 for Docker
echo -e "[wsl2]\nmemory=4GB\nprocessors=4\nswap=2GB\nlocalhostForwarding=true" > ~/.wslconfig
# Restart WSL2
wsl --shutdown
This guide provides a complete workflow for downloading Docker images from Azure Pipeline artifacts and importing them into WSL2 without using any Docker registries.
Maven
Configure proxy with settings.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<profiles>
<!-- Single default profile with proxy and SSL insecure settings -->
<profile>
<id>corporate-proxy</id>
<activation>
<!-- Activate this profile by default -->
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<properties>
<!-- Disable SSL certificate checks for HTTP repositories -->
<maven.wagon.http.ssl.insecure>true</maven.wagon.http.ssl.insecure>
</properties>
<proxies>
<proxy>
<id>default-proxy</id>
<active>true</active>
<protocol>http</protocol>
<host>corporate-proxy.example.com</host>
<port>8080</port>
<username>proxyuser</username>
<password>proxypass</password>
<nonProxyHosts>localhost|*.internal.example.com</nonProxyHosts>
</proxy>
</proxies>
</profile>
</profiles>
</settings>