Scala 2 Closures and Higher-Order Functions
Explore comprehensive Scala 2 functional programming fundamentals grounded in mathematical theory. This guide covers pure functions that ensure determinism and referential transparency, enabling equational reasoning and safe parallelization. Discover higher-order functions like map, filter, and fold that accept or return functions as first-class values. Master function composition techniques using compose and andThen operators to build complex pipelines. Learn currying—the mathematical transformation of multi-argument functions into sequences of single-argument functions. Understand immutability principles, side-effect elimination, and how these concepts form the backbone of scalable, testable Scala applications through category theory and lambda calculus foundations.
- Pure Functions
- Higher-Order Functions
- Core building blocks of FP
- 1. Partial Application
- 2. Currying
- 3. Uncurrying
- 4. Composition
- Scala Type Classes
Functional Programming (FP) is a programming paradigm based on mathematical functions where computation is treated as the evaluation of mathematical functions avoiding changing state and mutable data. This guide explores five fundamental FP concepts in Scala 2 with their mathematical foundations.
Core Principles of Functional Programming
- Functions are first-class values: Functions can be passed as arguments, returned from other functions, and assigned to variables
- Immutability: Data structures don’t change after creation
- No side effects: Pure functions don’t modify external state
- Referential Transparency: Expressions can be replaced by their values without changing program behavior
Pure Functions
Mathematical Definition
A pure function is a mathematical function where:
\[f: A \rightarrow B\]Such that:
- Determinism: $\forall x \in A, f(x)$ always produces the same output $y \in B$
- No Side Effects: $f$ doesn’t modify any state outside its scope
- Referential Transparency: For any program $p$, all occurrences of $f(x)$ can be replaced by its result without changing $p$’s meaning
Formal Definition
Referential Transparency (RT): An expression $e$ is referentially transparent if, for all programs $p$, all occurrences of $e$ in $p$ can be replaced by the result of evaluating $e$ without affecting the meaning of $p$.1
Purity: A function $f$ is pure if the expression $f(x)$ is referentially transparent for all referentially transparent $x$.1
Mathematical Properties
---
config:
look: neo
theme: default
---
graph TB
A[Pure Function Properties] --> B[Determinism]
A --> C[No Side Effects]
A --> D[Referential Transparency]
B --> E["∀x: f(x) = constant"]
C --> F["No I/O, mutations, or exceptions"]
D --> G["Can substitute f(x) with its result"]
style A fill:#e1f5ff
style B fill:#fff4e1
style C fill:#fff4e1
style D fill:#fff4e1
Substitution Model
Pure functions enable equational reasoning through the substitution model:
\[\begin{align} \text{Given: } & f(x) = x^2 \\ \text{Then: } & f(3) + f(3) \\ & = 9 + f(3) \quad \text{(substitute first)} \\ & = 9 + 9 \quad \text{(substitute second)} \\ & = 18 \end{align}\]for example,
import pprint._
// Update the REPL's printer configuration
repl.pprinter.update(
repl.pprinter().copy(
additionalHandlers = {
// Check if the object is a function/lambda by looking at its class name
case x: AnyRef if x.getClass.getName.contains("$$Lambda") =>
Tree.Literal("<function>")
}
)
)
import pprint._
// Update the REPL's printer configuration
// Pure Function - Always returns the same output for the same input
def square(x: Int): Int = x * x
// Test purity
val result1 = square(5) // 25
val result2 = square(5) // 25
// result1 == result2 always true
defined function square
result1: Int = 25
result2: Int = 25
Mathematical proof:
square(5) = 5 * 5 = 25
NOTE: Can always replace square(5) with 25
Pure function using internal mutable state (hidden from outside).
Pure Functions in Mathematics
| Mathematical Concept | Scala Example | Property |
|---|---|---|
| $f(x) = x + 1$ | def inc(x: Int) = x + 1 |
Successor function |
| $f(x, y) = x + y$ | def add(x: Int, y: Int) = x + y |
Addition |
| $f(x) = x^2$ | def square(x: Int) = x * x |
Quadratic |
| $f(s) = |s|$ | def length(s: String) = s.length |
String length |
| $f(x) = e^x$ | def exp(x: Double) = math.exp(x) |
Exponential |
Key Benefits of Pure Functions
- Testability: Easy to test - same input always produces the same output
- Parallelisation: Can safely run in parallel (no shared mutable state)
- Memoization: Results can be cached
- Reasoning: Enable algebraic reasoning and equational substitution
- Composition: Can combine pure functions to create complex behaviour
---
config:
look: neo
theme: default
---
mindmap
root((Pure Functions))
Benefits
Easy Testing
Predictable
No Mocks Needed
Parallelization
Thread Safe
No Race Conditions
Caching
Memoization
Performance
Properties
Deterministic
No Side Effects
Referential Transparency
Applications
Mathematical Computations
Data Transformations
Functional Pipelines
Higher-Order Functions
Morphisms are simply arrows or mappings between objects in a category. Think of them as generalized functions. When we say “objects are types and morphisms are functions”:
- Objects = Types (
Int,String,List[A], etc.) - Morphisms = Functions between those types
def length: String => Int
This is a morphism from the object String to the object Int.
String —-length—-> Int (object) (morphism) (object)
A higher-order function like map is a morphism in a “higher” category:
def map[A, B](f: A => B): List[A] => List[B]
// or curried version
def map[A, B](f: A => B)(xs: List[A]): List[B]
Here:
- Objects are themselves function types:
(A => B),(List[A] => List[B]) - Morphism is
map, which maps between these function objects
(A => B) ----map----> (List[A] => List[B])
HOF Mathematical Definition
A higher-order function (HOF) is a function that:
- Takes one or more functions as arguments, or
- Returns a function as its result
In category theory, HOFs are morphisms in the category of functions where objects are types and morphisms are functions.2
Type Theory Foundation of HOF
In the simply typed lambda calculus, if $\tau_1, \tau_2, \tau_3$ are types:
\[f: (\tau_1 \rightarrow \tau_2) \rightarrow \tau_3 \text{ is a HOF}\]This means $f$ accepts a function of type $\tau_1 \rightarrow \tau_2$ and produces a value of type $\tau_3$.
Examples
- Map operation (Functor)
- Filter operation
- Fold operation:
Example 1: Map - The Functor HOF3
Map operation (Functor):
\[\text{map}: (A \rightarrow B) \rightarrow [A] \rightarrow [B]\]This reads as: “
maptakes a function from A to B, then takes a list of A’s, and returns a list of B’s”.
The arrows represent currying - map doesn’t take all arguments at once, but returns functions:
- Takes
(A → B)- a function from type A to type B - Returns a function that takes
[A]- a list of A’s - Which returns
[B]- a list of B’s
Behaviour:
\[\text{map}\ f\ [x_1, x_2, ..., x_n] = [f(x_1), f(x_2), ..., f(x_n)]\]Apply function f to each element in the list.
The map applies a function to each element
def map[A, B](f: A => B)(xs: List[A]): List[B] = xs match {
case Nil => Nil
case head :: tail => f(head) :: map(f)(tail)
}
Type Parameters: [A, B] - generic types matching the math notation
Curried Syntax: Two parameter lists (f: A => B)(xs: List[A]) implements the curried arrows:
- First takes function
f: A => B(matchingA → B) - Then takes list
xs: List[A](matching[A]) - Returns
List[B](matching[B])
The recursive case implements the mathematical definition:
f(head)- apply f to first element (likef(x₁))map(f)(tail)- recursively map over remaining elements (like[f(x₂), ..., f(xₙ)])::- cons operator joins them together
Example execution is
map(x => x * 2)(List(1, 2, 3))
Traces to:
f(1) :: map(f)(List(2, 3))
2 :: f(2) :: map(f)(List(3))
2 :: 4 :: f(3) :: map(f)(Nil)
2 :: 4 :: 6 :: Nil
List(2, 4, 6)
This matches the math: map (*2) [1,2,3] = [2, 4, 6] ✓
// Using map
val numbers = List(1, 2, 3)
val squared = map((x: Int) => x * 2)(numbers)
// Result: List(1, 4, 9, 16, 25)
// Mathematical property (Functor law):
// map(id) == id
// map(f ∘ g) == map(f) ∘ map(g)
numbers: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
squared: List[Int] = List(2, 4, 6)
Scala standard library usage
val nums = List(1, 2, 3)
// map with named function
def double(x: Int): Int = x * 2
nums.map(double) // List(2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
nums: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3)
defined function double
res14_2: List[Int] = List(2, 4, 6)
Example 2: Filter - Predicate-Based Selection3
filter keeps elements satisfying a predicate
\[\text{filter}: (A \rightarrow \text{Bool}) \rightarrow [A] \rightarrow [A]\]This reads as: “
filtertakes a predicate function from A to Boolean, then takes a list of A’s, and returns a list of A’s”
Key difference from map: the input and output list types are the same ([A] → [A]) because we’re selecting elements, not transforming them.
The currying structure:
- Takes
(A → Bool)- a predicate function that tests elements - Returns a function that takes
[A]- a list of A’s - Which returns
[A]- a filtered list of A’s
Behaviour (List Comprehension):
This is list comprehension notation meaning: “build a list containing all elements x drawn from xs where the predicate p(x) is true”
def filter[A](p: A => Boolean)(xs: List[A]): List[A] = xs match {
case Nil => Nil
case head :: tail =>
if (p(head)) head :: filter(p)(tail)
else filter(p)(tail)
}
defined function filter
Type Parameter: [A] - single generic type (input and output are same type)
Curried Syntax: (p: A => Boolean)(xs: List[A]) implements:
- First takes predicate
p: A => Boolean(matchingA → Bool) - Then takes list
xs: List[A](matching[A]) - Returns
List[A](matching[A])
Pattern Matching Implementation:
The recursive logic implements the list comprehension:
- Test:
if (p(head))- checks if predicate holds for current element - Include:
head :: filter(p)(tail)- keep element and continue - Exclude:
filter(p)(tail)- skip element and continue - Eventually builds a list of only elements where
p(x)was true
// Using filter
val numbers = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
// Keep even numbers
val evens = filter((x: Int) => x % 2 == 0)(numbers)
// Result: List(2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
// Mathematical definition as list comprehension:
// filter p xs = [x | x ← xs, p x]
numbers: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10)
evens: List[Int] = List(2, 4, 6, 8, 10)
Example Execution
filter(x => x > 2)(List(1, 2, 3, 4))
Traces to:
p(1) = false → filter(p)(List(2, 3, 4))
p(2) = false → filter(p)(List(3, 4))
p(3) = true → 3 :: filter(p)(List(4))
p(4) = true → 3 :: 4 :: filter(p)(Nil)
3 :: 4 :: Nil
List(3, 4)
Scala Standard library usage:
// Practical examples
val numbers = List(-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// Filter positive numbers
numbers.filter(_ > 0) // List(1, 2, 3)
// Filter even numbers
numbers.filter(x => x % 2 == 0) // List(-2, 0, 2, 4)
// Chain filter operations
numbers
.filter(_ > 0) // List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
.filter(_ % 2 == 0) // List(2, 4)
numbers: List[Int] = List(-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
res18_1: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
res18_2: List[Int] = List(-2, 0, 2, 4)
res18_3: List[Int] = List(2, 4)
This matches the math: \(\text{filter}\ (>2)\ [1,2,3,4] = [x\ |\ x \leftarrow [1,2,3,4], x > 2] = [3, 4]\)
Example 3: Fold - Reduction Operations3
foldr - right-associative fold
\[\text{foldr}: (A \rightarrow B \rightarrow B) \rightarrow B \rightarrow [A] \rightarrow B\]This reads as: “
foldrtakes a combining function, then an initial value, then a list, and returns a single accumulated value”
The currying structure (three levels):
- Takes
(A → B → B)- a combining function that takes an element of type A and an accumulator of type B, returning a new B - Then takes
B- an initial/accumulator value - Then takes
[A]- a list of A’s - Returns
B- a single folded result
Behaviour (Right-Associative):
\[\text{foldr}\ (\oplus)\ a\ [x_1, x_2, ..., x_n] = x_1 \oplus (x_2 \oplus ... (x_n \oplus a))\]Works right-to-left, with parentheses showing association from the right. The rightmost element xₙ is combined with the initial value first, then that result is combined with xₙ₋₁, and so on.
def foldr[A, B](f: (A, B) => B)(z: B)(xs: List[A]): B = xs match {
case Nil => z
case head :: tail => f(head, foldr(f)(z)(tail))
}
// Mathematical notation:
// foldr (⊕) a [x₁, x₂, ..., xₙ] = x₁ ⊕ (x₂ ⊕ ... (xₙ ⊕ a))
defined function foldr
Type Parameters: [A, B] - two types (list elements and accumulator can differ)
Three Parameter Lists (Curried):
(f: (A, B) => B)- combining function (matchingA → B → B)(z: B)- initial/”zero” value (matching theB)(xs: List[A])- input list (matching[A])- Returns
B- folded result
The recursive case implements right-associativity:
foldr(f)(z)(tail)- first recursively fold the tail (processes right side)f(head, ...)- then combine head with that result (processes left side)- This creates the structure:
head ⊕ (recursive_result)
Example Execution
// Practical fold examples
val numbers = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// Product using foldRight
val product = numbers.foldRight(1)(_ * _) // 120
// Evaluation: 1 * (2 * (3 * (4 * (5 * 1))))
numbers: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
product: Int = 120
see the trace below for the following
foldr((x: Int, acc: Int) => x + acc)(0)(List(1, 2, 3))
res34: Int = 6
Traces to:
f(1, foldr(f)(0)(List(2, 3)))
f(1, f(2, foldr(f)(0)(List(3))))
f(1, f(2, f(3, foldr(f)(0)(Nil))))
f(1, f(2, f(3, 0)))
f(1, f(2, 3))
f(1, 5)
6
This matches the math: \(\text{foldr}\ (+)\ 0\ [1,2,3] = 1 + (2 + (3 + 0)) = 1 + (2 + 3) = 1 + 5 = 6\) ✓
Visualising Right Association
For foldr (⊕) a [x₁, x₂, x₃]:
x₁ ⊕ (x₂ ⊕ (x₃ ⊕ a))
│ │ │
│ │ └─ combines first
│ └──────── combines second
└─────────────── combines last
foldl - left-associative fold
\[\text{foldl}: (B \rightarrow A \rightarrow B) \rightarrow B \rightarrow [A] \rightarrow B\]This reads as: “
foldltakes a combining function, then an initial value, then a list, and returns a single accumulated value”
The currying structure (three levels):
- Takes
(B → A → B)- a combining function that takes an accumulator of type B and an element of type A, returning a new B- Note: Arguments are reversed compared to
foldr!
- Note: Arguments are reversed compared to
- Then takes
B- an initial/accumulator value - Then takes
[A]- a list of A’s - Returns
B- a single folded result
Behaviour (Left-Associative):
\[\text{foldl}\ (\oplus)\ a\ [x_1, x_2, ..., x_n] = ((...((a \oplus x_1) \oplus x_2) ...) \oplus x_n)\]Works left-to-right, with parentheses showing association from the left. The leftmost element x₁ is combined with the initial value a first, then that result is combined with x₂, and so on.
// foldl - left-associative fold
def foldl[A, B](f: (B, A) => B)(z: B)(xs: List[A]): B = xs match {
case Nil => z
case head :: tail => foldl(f)(f(z, head))(tail)
}
// Mathematical notation:
// foldl (⊕) a [x₁, x₂, ..., xₙ] = (((a ⊕ x₁) ⊕ x₂) ... ⊕ xₙ)
defined function foldl
Type Parameters: [A, B] - two types (list elements and accumulator can differ)
Three Parameter Lists (Curried):
(f: (B, A) => B)- combining function with accumulator first (matchingB → A → B)(z: B)- initial/”zero” value (matching theB)(xs: List[A])- input list (matching[A])- Returns
B- folded result
Example Execution
The recursive case implements left-associativity:
f(z, head)- first combine accumulator with head (processes left side)foldl(f)(...)(tail)- then recursively fold tail with new accumulator- This creates the structure:
(previous_result) ⊕ head
foldl((acc: Int, x: Int) => acc + x)(0)(List(1, 2, 3)) // traced
res36: Int = 6
Traces to:
foldl(f)(f(0, 1))(List(2, 3))
foldl(f)(1)(List(2, 3))
foldl(f)(f(1, 2))(List(3))
foldl(f)(3)(List(3))
foldl(f)(f(3, 3))(Nil)
foldl(f)(6)(Nil)
6
This matches the math: \(\text{foldl}\ (+)\ 0\ [1,2,3] = ((0 + 1) + 2) + 3 = (1 + 2) + 3 = 3 + 3 = 6\) ✓
Visualising Left Association
For foldl (⊕) a [x₁, x₂, x₃]:
((a ⊕ x₁) ⊕ x₂) ⊕ x₃
│ │ │
│ │ └─ combines last
│ └──────── combines second
└─────────────────── combines first
For example, Building a reversed list with foldLeft
val reversed = numbers.foldLeft(List.empty[Int])((acc, x) => x :: acc)
// Result: List(5, 4, 3, 2, 1)
reversed: List[Int] = List(5, 4, 3, 2, 1)
Scala Standard library usage:
// Practical fold examples
val numbers = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
// Sum using foldLeft
val sum = numbers.foldLeft(0)(_ + _) // 15
// Evaluation: ((((0 + 1) + 2) + 3) + 4) + 5
// Product using foldRight
val product = numbers.foldRight(1)(_ * _) // 120
// Evaluation: 1 * (2 * (3 * (4 * (5 * 1))))
// Building a reversed list with foldLeft
val reversed = numbers.foldLeft(List.empty[Int])((acc, x) => x :: acc)
// Result: List(5, 4, 3, 2, 1)
numbers: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
sum: Int = 15
product: Int = 120
reversed: List[Int] = List(5, 4, 3, 2, 1)
Defining common operations with fold
def sum(xs: List[Int]): Int = xs.foldRight(0)(_ + _)
def product(xs: List[Int]): Int = xs.foldRight(1)(_ * _)
def length[A](xs: List[A]): Int = xs.foldRight(0)((_, acc) => acc + 1)
def concatenate[A](xss: List[List[A]]): List[A] = xss.foldRight(List.empty[A])(_ ++ _)
// Example usage
sum(List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) // 15
product(List(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)) // 120
length(List('a', 'b', 'c')) // 3
concatenate(List(List(1,2), List(3,4))) // List(1, 2, 3, 4)
defined function sum
defined function product
defined function length
defined function concatenate
res37_4: Int = 15
res37_5: Int = 120
res37_6: Int = 3
res37_7: List[Int] = List(1, 2, 3, 4)
Comparing foldr vs foldl
foldr: x₁ ⊕ (x₂ ⊕ (x₃ ⊕ a))
- Right-associative
- Processes right side first (via recursion)
- Function signature:
(A, B) => B
foldl: ((a ⊕ x₁) ⊕ x₂) ⊕ x₃
- Left-associative
- Processes left side first (via accumulator)
- Function signature:
(B, A) => B
Example Where Order Matters
// Division is NOT associative
foldr((x: Int, acc: Int) => x / acc)(1)(List(8, 4, 2))
// 8 / (4 / (2 / 1)) = 8 / (4 / 2) = 8 / 2 = 4
foldl((acc: Int, x: Int) => acc / x)(64)(List(4, 2, 2))
// ((64 / 4) / 2) / 2 = (16 / 2) / 2 = 8 / 2 = 4
res28_0: Int = 4
res28_1: Int = 4
Different structure, potentially different results!
Example: Building a Reversed List
foldl((acc: List[Int], x: Int) => x :: acc)(Nil)(List(1, 2, 3))
res29: List[Int] = List(3, 2, 1)
((Nil :: 1) :: 2) :: 3
(List(1) :: 2) :: 3
List(2, 1) :: 3
List(3, 2, 1)
This reverses the list! In fact, foldl (flip (::)) Nil xs = reverse xs
Insights:
foldlis tail-recursive in this implementation - the recursive call is the last operation, making it more memory efficient- Left-associative: processes list from left to right via accumulator
- Accumulator-first: the function takes
(B, A)not(A, B)- accumulator is first argument - For associative operations (like
+,*),foldrandfoldlproduce the same result - For non-associative operations (like
-,/,::) they produce different results - In practice:
foldlis often preferred for efficiency (tail-recursive), butfoldrworks on infinite lists
Example 4: Custom HOFs
A HOF that applies a function n times.
The applyNTimes function implements repeated function composition or function exponentiation:
More explicitly:
- $f^0(x) = x$ (identity - apply 0 times)
- $f^1(x) = f(x)$ (apply once)
- $f^2(x) = f(f(x))$ (apply twice)
- $f^3(x) = f(f(f(x)))$ (apply three times)
- $f^n(x) = f(f^{n-1}(x))$ (recursive definition)
in Mathematics
\[\text{applyNTimes}: (A \rightarrow A) \rightarrow \mathbb{N} \rightarrow (A \rightarrow A)\]Reads as: “Takes an endomorphism (function from A to itself) and a natural number, returns another endomorphism”
Type Analysis
- Input 1:
f: A => A- an endomorphism (function that maps type A to itself) - Input 2:
n: Int- number of times to compose f - Output:
A => A- a new function that applies f exactly n times
The loop helper function:
This implements: $\text{loop}(x, n) = f^n(x)$
def applyNTimes[A](f: A => A, n: Int): A => A = {
def loop(x: A, remaining: Int): A = {
if (remaining <= 0) x
else loop(f(x), remaining - 1)
}
(x: A) => loop(x, n)
}
defined function applyNTimes
Execution trace for loop(x, 3):
loop(x, 3)
→ loop(f(x), 2)
→ loop(f(f(x)), 1)
→ loop(f(f(f(x))), 0)
→ f(f(f(x)))
val increment: Int => Int = x => x + 1
val addFive = applyNTimes(increment, 5)
// addFive is equivalent to: x => x + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1
addFive(10) // Output: 15
increment: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd40$Helper$$Lambda$2754/0x000000012c898bc8@7d57e5ae
addFive: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd38$Helper$$Lambda$2750/0x000000012c897908@612c3a59
res40_2: Int = 15
Function design properties:
1: Identity Law
\(\text{applyNTimes}(f, 0) = \text{id}\) Where $\text{id}(x) = x$ for all $x$
val identityFunc = applyNTimes(increment, 0)
identityFunc(10)
identityFunc: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd38$Helper$$Lambda$2750/0x000000012c897908@6a7a462
res43_1: Int = 10
2: Composition Law
\[\text{applyNTimes}(f, m + n) = \text{applyNTimes}(f, m) \circ \text{applyNTimes}(f, n)\]val add3 = applyNTimes(increment, 3)
val add5 = applyNTimes(increment, 5)
val add8 = applyNTimes(increment, 8)
// These are equivalent:
add8(10) // 18
add5(add3(10)) // 18
add3: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd38$Helper$$Lambda$2750/0x000000012c897908@447f7c8f
add5: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd38$Helper$$Lambda$2750/0x000000012c897908@150f8d6c
add8: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd38$Helper$$Lambda$2750/0x000000012c897908@7ddc39a
res44_3: Int = 18
res44_4: Int = 18
3: Recursive Structure \(f^n = f \circ f^{n-1}\)
This is exactly what the loop function implements through tail recursion.
In category theory, applyNTimes works with endomorphisms in a category:
- Objects: Types (like
Int,String, etc.) - Morphisms: Functions between types
- Endomorphism: A morphism from an object to itself (
A => A)
The function creates a monoid structure:
- Binary operation: Function composition $\circ$
- Identity element: $f^0 = \text{id}$
- Closure: $f^m \circ f^n = f^{m+n}$
Tail Recursion Optimisation
The loop function is tail-recursive because:
- The recursive call is the last operation
- No additional computation after the recursive call returns
- Scala compiler can optimise it to a loop (with
@tailrecannotation)
import scala.annotation.tailrec
def applyNTimes[A](f: A => A, n: Int): A => A = {
@tailrec
def loop(x: A, remaining: Int): A = {
if (remaining <= 0) x
else loop(f(x), remaining - 1)
}
(x: A) => loop(x, n)
}
import scala.annotation.tailrec
defined function applyNTimes
Composition in Scala
Understanding Function Composition in Scala
Function composition forms a category:
Category of Types and Functions:
- Objects: Types (
Int,String,Boolean, etc.) - Morphisms: Functions between types
- Composition: Function composition operator
- Identity: Identity function for each type
Category Laws:
- Associativity: $(f \circ g) \circ h = f \circ (g \circ h)$
- Identity: $f \circ \text{id}_A = f = \text{id}_B \circ f$ for $f: A \to B$
This makes function composition a fundamental operation in functional programming.
In mathematics, function composition is denoted by the symbol $\circ$ (circle):
\[(f \circ g)(x) = f(g(x))\]Read as: “f composed with g, applied to x, equals f of g of x”
Key points:
- Apply $g$ first to $x$
- Then apply $f$ to the result
- The right function ($g$) is applied first
- Composition flows right-to-left
x → [g] → g(x) → [f] → f(g(x))
apply g first then apply f
For composition $f \circ g$ to be valid: \(f: B \rightarrow C\) \(g: A \rightarrow B\) \(f \circ g: A \rightarrow C\)
The output type of $g$ must match the input type of $f$.
def compose[A, B, C](f: B => C, g: A => B): A => C = {
(x: A) => f(g(x))
}
defined function compose
Type Analysis
Type signature: \(\text{compose}: (B \rightarrow C) \rightarrow (A \rightarrow B) \rightarrow (A \rightarrow C)\)
- Parameter 1:
f: B => C- function that transforms B to C - Parameter 2:
g: A => B- function that transforms A to B - Returns:
A => C- a new function that transforms A to C
How It Works
The function returns a closure (lambda):
(x: A) => f(g(x))
This lambda:
- Takes an argument
xof typeA - Applies
gto get a value of typeB - Applies
fto get a final value of typeC
Examples:
val addOne = (x: Int) => x + 1
val double = (x: Int) => x * 2
val addOneThenDouble = compose(double, addOne)
addOneThenDouble(5)
addOne: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd49$Helper$$Lambda$2790/0x000000012c8a4000@54d5fa77
double: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd49$Helper$$Lambda$2791/0x000000012c8a43e8@27a2a472
addOneThenDouble: Int => Int = ammonite.$sess.cmd47$Helper$$Lambda$2786/0x000000012c89ed08@7da32905
res49_3: Int = 12
Type flow:
addOne: Int => Int(matchesA => Bwhere A=Int, B=Int)double: Int => Int(matchesB => Cwhere B=Int, C=Int)addOneThenDouble: Int => Int(resultingA => C)
Execution trace:
\[\begin{flalign*} \text{addOneThenDouble}(5) &= \text{double}(\text{addOne}(5)) \\ &= \text{double}(5 + 1) \\ &= \text{double}(6) \\ &= 6 \times 2 \\ &= 12 \end{flalign*}\]Scala provides two composition methods in the standard library:
| Concept | Mathematical | Scala compose |
Scala andThen |
|---|---|---|---|
| Notation | $f \circ g$ | f compose g |
g andThen f |
| Meaning | $f(g(x))$ | f(g(x)) |
f(x) then g |
| Flow | Right-to-left | Right-to-left | Left-to-right |
| Natural? | Math traditional | Math traditional | More intuitive |
1: compose - Right-to-Left (Mathematical Order)
val f = addOne compose double
// Equivalent to: (x: Int) => addOne(double(x))
f: Int => Int = scala.Function1$$Lambda$2796/0x000000012c8a1118@28b3e02d
mathamatically
\(f = \text{addOne} \circ \text{double}\) \(f(x) = \text{addOne}(\text{double}(x))\)
Execution:
f(5) // addOne(double(5))
// = addOne(5 * 2)
// = addOne(10)
// = 10 + 1
// = 11
Flow diagram:
5 → [double] → 10 → [addOne] → 11
apply first apply second
2: andThen - Left-to-Right (Pipeline Order)
val g = addOne andThen double
// Equivalent to: (x: Int) => double(addOne(x))
g: Int => Int = scala.Function1$$Lambda$766/0x000000012c5360b0@7d14a8aa
mathamatically
\(g = \text{double} \circ \text{addOne}\) \(g(x) = \text{double}(\text{addOne}(x))\)
Execution:
g(5) // double(addOne(5))
// = double(5 + 1)
// = double(6)
// = 6 * 2
// = 12
Flow diagram:
5 → [addOne] → 6 → [double] → 12
apply first apply second
HOF Mathematical Properties
| Property | Mathematical Form | Code Example |
|---|---|---|
| Map Composition | $\text{map}(f \circ g) = \text{map}(f) \circ \text{map}(g)$ | xs.map(g).map(f) == xs.map(f compose g) |
| Map Identity | $\text{map}(\text{id}) = \text{id}$ | xs.map(x => x) == xs |
| Filter Composition | $\text{filter}(p) \circ \text{filter}(q) = \text{filter}(q) \circ \text{filter}(p)$ | xs.filter(p).filter(q) == xs.filter(q).filter(p) |
| Fold Fusion | $\text{map}(f) \circ \text{fold}(g)(z) = \text{fold}(g \circ f)(z)$ | Optimization technique |
For-Comprehensions and HOFs
The for comprehension4 is syntactic sugar for HOF chains
for {
x <- List(1,2,3)
y <- List(10, 20)
if x * y > 10 // Guard
} yield x * y
res53: List[Int] = List(20, 20, 40, 30, 60)
Desugars to:
List(1,2,3).flatMap(x => List(10,20).filter( y => x * y > 10).map( y => x * y))
res60: List[Int] = List(20, 20, 40, 30, 60)
Type Signatures of Common HOFs
| Function | Type Signature | Description |
|---|---|---|
map |
[A, B](f: A => B): List[A] => List[B] |
Apply function to each element |
filter |
[A](p: A => Boolean): List[A] => List[A] |
Keep elements satisfying predicate |
foldLeft |
[A, B](z: B)(f: (B, A) => B): List[A] => B |
Left-associative reduction |
foldRight |
[A, B](z: B)(f: (A, B) => B): List[A] => B |
Right-associative reduction |
flatMap |
[A, B](f: A => List[B]): List[A] => List[B] |
Map then flatten |
find |
[A](p: A => Boolean): List[A] => Option[A] |
Find first matching element |
exists |
[A](p: A => Boolean): List[A] => Boolean |
Check if any element matches |
forall |
[A](p: A => Boolean): List[A] => Boolean |
Check if all elements match |
Core building blocks of FP
There are 4 building blocks:
-
Partial Application: Partial application is the process of taking a function that accepts multiple arguments, providing values for some of them, and producing a new function that expects the rest of the arguments. Think of it as “pre-filling” data.
def partial[A, B, C](a:A, f:(A, B) => C): B = b => f(a, b) -
Currying: Currying transforms a function that takes multiple arguments at once (like (A, B)) into a chain of functions that each take exactly one argument. It changes the function’s shape, not its values.
def partial[A, B, C] (a:A, f: (A, B) => C): B => C = b => f(a, b) -
Uncurrying: Uncurrying is the reverse of currying. It takes a chain of functions (a function that returns a function) and collapses them into a single function that takes multiple arguments simultaneously.
def uncurry[A, B, C](f: A => B => C): (A, B) => C = (a, b) => f(a)(b) -
Composition: Function composition allows you to pipe the output of one function directly into the input of another. It glues two functions together to create a pipeline.
def compose[A, B, C](f: B => C, g: A => B): A => C = a => f(g(a))
1. Partial Application
Partial Application is the process of fixing a specific number of arguments to a function, producing a new function of smaller arity (taking fewer arguments).
def partial[A, B, C] (a:A, f: (A, B) => C): B => C =
b => f(a, b)
defined function partial
For example:
val add = (x: Int, y: Int) => x + y
val add5 = partial(5, add)
add5(10)
add: (Int, Int) => Int = <function>
add5: Int => Int = <function>
res6_2: Int = 15
When we have a function that appears to take multiple arguments, such as f(x, y), we can think of it in two ways. Based onthe Lambda Calculus:
The Product Type View: The function takes a tuple (a pair) of arguments.
\[f:\left( A\times B\right) \rightarrow C\]The Partial Application View: If we fix the first argument $a_{0}$ (where $a_{0}\in A$), we effectively create a new function $g$ that only relies on $b$.
\[g\left( b\right) =f\left( a_{0},b\right)\]Here, $g$ is the partially applied version of $f$. It maps $B\rightarrow C$.
2. Currying
Mathematically:
Currying is the transformation of a function with multiple arguments into a sequence of functions, each taking a single argument.5
Named after mathematician Haskell Curry, currying transforms:
\[f: A \times B \times C \rightarrow D\]Into:
\[\text{curry}(f): A \rightarrow (B \rightarrow (C \rightarrow D))\]This isomorphism is expressed as:
\[\text{Hom}(A \times B, C) \cong \text{Hom}(A, C^B)\]Where $C^B$ denotes the exponential object (function type $B \rightarrow C$).
for examples
def curry[A, B, C](f: (A, B) => C): A => (B => C) =
a => b => f(a, b)
defined function curry
val multiply = (x: Int, y: Int) => x * y
val curriedMultiply = curry(multiply)
curriedMultiply(10)(2)
multiply: (Int, Int) => Int = <function>
curriedMultiply: Int => Int => Int = <function>
res9_2: Int = 20
Manual Currying[^5]
// Regular multi-parameter function
def add(x: Int, y: Int, z: Int): Int = x + y + z
// Manually curried version
def addCurried(x: Int): Int => Int => Int = {
(y: Int) => {
(z: Int) => {
x + y + z
}
}
}
// Using the curried version
val addFive = addCurried(5) // Returns function: Int => Int => Int
val addFiveSeven = addFive(7) // Returns function: Int => Int
val result = addFiveSeven(3) // Returns: 15
// Or in one line:
addCurried(5)(7)(3) // 15
// Mathematical evaluation:
// addCurried(5)(7)(3)
// = ((x => y => z => x+y+z)(5))(7)(3)
// = (y => z => 5+y+z)(7)(3)
// = (z => 5+7+z)(3)
// = 5+7+3 = 15
defined function add
defined function addCurried
addFive: Int => Int => Int = <function>
addFiveSeven: Int => Int = <function>
result: Int = 15
res7_5: Int = 15
Scala’s Built-in Currying5
// Scala syntax for curried functions (multiple parameter lists)
def multiply(x: Int)(y: Int)(z: Int): Int = x * y * z
// Partial application at each level
val timesTen = multiply(10) _ // Int => Int => Int
val timesTenFive = timesTen(5) // Int => Int
val result = timesTenFive(2) // 100
// Can also apply all at once
multiply(10)(5)(2) // 100
// Type signatures:
// multiply: (x: Int)(y: Int)(z: Int): Int
// multiply(10): Int => Int => Int
// multiply(10)(5): Int => Int
// multiply(10)(5)(2): Int
defined function multiply
timesTen: Int => Int => Int = <function>
timesTenFive: Int => Int = <function>
result: Int = 100
res8_4: Int = 100
3. Uncurrying
The inverse transformation:
\[\text{uncurry}: (A \rightarrow (B \rightarrow C)) \rightarrow ((A \times B) \rightarrow C)\]def uncurry[A, B, C](f: A => B => C): (A, B) => C =
(a,b) => f(a)(b)
defined function uncurry
For example:
// A function that is already curried
val curriedSubtract = (x: Int) => (y: Int) => x - y
// Convert it back to a standard (Int, Int) => Int function
val subtract = uncurry(curriedSubtract)
subtract(10, 3)
curriedSubtract: Int => Int => Int = <function>
subtract: (Int, Int) => Int = <function>
res11_2: Int = 7
Converting Between Curried and Uncurried1
// Example usage
val add: (Int, Int) => Int = (x, y) => x + y
val addCurried: Int => Int => Int = curry(add)
val addUncurried: (Int, Int) => Int = uncurry(addCurried)
// Test
add(3, 4) // 7
addCurried(3)(4) // 7
addUncurried(3, 4) // 7
add: (Int, Int) => Int = <function>
addCurried: Int => Int => Int = <function>
addUncurried: (Int, Int) => Int = <function>
res14_3: Int = 7
res14_4: Int = 7
res14_5: Int = 7
built-in curry functions:
// Function1 has built-in curried method
val multiply = (x: Int, y: Int, z: Int) => x * y * z
val multiplyCurried = multiply.curried
// Type: Int => Int => Int => Int÷
multiply: (Int, Int, Int) => Int = <function>
multiplyCurried: Int => Int => Int => Int = <function>
4. Composition
Glue 2 functions to create a pipeline. In compose(f, g), g runs first, then f. This is standard mathematical notation ($f \circ g$).
def compose[A, B, C](f: B => C, g: A => B): A => C =
a => f(g(a))
defined function compose
Examples:
val double = (i:Int) => i * 2
val num2str = (i: Int) => s"result is $i"
val pipeline = compose(num2str, double)
pipeline(2)
double: Int => Int = <function>
num2str: Int => String = <function>
pipeline: Int => String = <function>
res17_3: String = "result is 4"
Scala Type Classes
Type classes in Scala are a powerful design pattern that allows you to add new functionality to existing types without modifying their source code. They enable ad-hoc polymorphism - the ability to define behaviour for types after they’ve been created.
Let’s use a classic example: creating a “printable” or Show behaviour. We want to be able to call .show() on any type (Int, String, our own User class) to get a nice, formatted string representation.
- The Type Class Trait
This is the “contract.” It’s a generic trait that defines the behaviour you want to add. It takes a type parameter [A] representing the type we’re adding functionality to.
trait Show[A] {
def show(value: A): String
}
defined trait Show
- Type Class Instances
These are the concrete implementations of the trait for specific types. We mark them as
implicitso the compiler can find them automatically. These instances are often placed in the companion object of the type class trait. This makes them easy for the compiler to find (this is a common part of implicit resolution).
// Put instances in the companion object
object Show {
// Instance for Int
implicit val intShow: Show[Int] = new Show[Int] {
def show(value: Int): String = s"Int is: $value"
}
// Instance for String
implicit val stringShow: Show[String] = new Show[String] {
def show(value: String): String = s"String is: $value"
}
// Instance for a custom class we don't want to modify
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
implicit val personShow: Show[Person] = new Show[Person] {
def show(p: Person): String = s"${p.name} is ${p.age} years old."
}
}
defined object Show
Above are known as implicit values.
Type classes in Scala are implemented using implicit values and parameters, and, optionally, implicit classes. Scala language constructs correspond to the components of type classes as follows:
- traits: type classes;
- implicit values: type class instances;
- implicit parameters: type class use; and
- implicit classes: optional utilities that make type classes easier to use.
In the cats:
- interface objects
- interface syntax
- The Interface (Using the Type Class)
This is how you use the type class. There are two main ways:
Method 1: The “Interface” Function (Implicit Parameter)
This is a function that requires a type class instance, specified via an implicit parameter list.
// This function "asks" for an implicit Show[A] to be available
def printThing[A](value: A)(implicit shower: Show[A]): Unit = {
println(shower.show(value))
}
defined function printThing
When you call printThing(123), the compiler sees it needs a Show[Int]. It looks in the implicit scope, finds Show.intShow, and “injects” it as the shower parameter.
Method 2: Extension Methods (The “Pretty” Way)
This is the most common and ergonomic way. We use an implicit class (part of the “pimp my library” pattern) to make it look like the method is on the original type (e.g., 123.show()).
object ShowSyntax {
implicit class ShowOps[A](value: A) {
// This method requires an implicit Show[A] to be in scope
def show(implicit s: Show[A]): String = {
s.show(value) // delegates to the instance
}
}
}
defined object ShowSyntax
This implicit class wraps any type A and gives it a .show method. That method will only compile if the compiler can find an implicit instance of Show[A] to pass to it.
// --- How to use it ---
// Import the instances and the syntax to bring them into scope
import Show._
import ShowSyntax._
val john = Person("John", 30)
// The compiler finds the correct implicit instance for each type!
println(123.show) // Uses intShow
println("Hello".show) // Uses stringShow
println(john.show) // Uses personShowA
Int is: 123
String is: Hello
John is 30 years old.
import Show._
import ShowSyntax._
john: Person = Person(name = "John", age = 30)
Implicit Resolution
When you write 123.show:
123(anInt) doesn’t have a.showmethod.- The compiler looks for an
implicitconversion that does have a.showmethod. - It finds
ShowSyntax.ShowOps[A](which we imported). It wraps123to becomeShowOps[Int](123). - Now it can call
ShowOps[Int](123).show. - This
showmethod itself has an(implicit s: Show[Int])parameter. - The compiler searches for an
implicitvalue of typeShow[Int]. - It finds
Show.intShow(which we also imported) and secretly passes it to the method. - The final call is effectively
intShow.show(123).
If you tried to call .show on a type with no instance (e.g., List(1,2).show), you would get a compile-time error, which is the power of the type class pattern.
Example from the Cats book:
The JsonWriter is the type class for serialising to JSON (explained in the Cats6):
object JsonModel {
sealed trait MyJson
final case class JsObject(get: Map[String, MyJson]) extends MyJson
final case class JsString(get: String) extends MyJson
final case class JsNumber(get: Double) extends MyJson
final case object JsNull extends MyJson
// Example model to demonstrate
final case class Employee(name: String, email: String)
// type class
trait JsonWriter[A] {
def write(value: A): MyJson
}
}
import JsonModel._
// implicit values: type class instances
object JsonWriterInstances {
implicit val stringWriter: JsonWriter[String] = new JsonWriter[String] {
def write(value: String): MyJson = JsString(value)
}
implicit val employeeWriter: JsonWriter[Employee] = new JsonWriter[Employee] {
def write(value: Employee): MyJson = JsObject(
Map("name" -> JsString(value.name)
,"email" -> JsString(value.email)))
}
// ... implement others to return such as JsNumber
}
// companion object
object MyJson {
// interface object
def toJson[A](value: A)(implicit w: JsonWriter[A]): MyJson = w.write(value)
}
import JsonWriterInstances._
MyJson.toJson(Employee("Ojitha", "ojitha@test.com")) //implicit scope applied
defined object JsonModel
import JsonModel._
defined object JsonWriterInstances
defined object MyJson
import JsonWriterInstances._
res1_5: MyJson = JsObject(
get = Map(
"name" -> JsString(get = "Ojitha"),
"email" -> JsString(get = "ojitha@test.com")
)
)
// interface syntax
object JsonSyntax {
implicit class JsonWriterOps[A](value: A) {
def convert2Json(implicit w: JsonWriter[A]): MyJson = w.write(value)
}
}
import JsonWriterInstances._
import JsonSyntax._
Employee("Ojitha", "ojitha@test.com").convert2Json
defined object JsonSyntax
import JsonWriterInstances._
import JsonSyntax._
res3_3: MyJson = JsObject(
get = Map(
"name" -> JsString(get = "Ojitha"),
"email" -> JsString(get = "ojitha@test.com")
)
)
Working with type classes in Scala means working with implicit values and implicit parameters. Placing instances in a companion object to the type class has special significance in Scala because it plays into something called implicit scope.
Implicit Scope
The implicit scope which roughly consists of:
- local or inherited definitions
- imported definitions
- definitions in the companion object of the type class or the parameter type (in this case
JsonWriterorString).
Definitions are only included in implicit scope if they are tagged with the implicit keyword.
Type class instances can be placed roughly in four ways:
- In an object (eg:
JasonWriterInstances): need to import - In a trait: using inheritance
- In the companion object of the Type Class
- In the companion object of the parameter type
Type class instances can be defined in two ways:
- concrete instances as
implicit val - by defining
implicitmethods to construct instances from other type class instances
implicit def optionWriter[A](implicit writer: JsonWriter[A]): JsonWriter[Option[A]] =
new JsonWriter[Option[A]] {
def write(option: Option[A]): MyJson = option match {
case Some(value) => writer.write(value)
case None => JsNull
}
}
defined function optionWriter
MyJson.toJson(Option("A string"))
res5: MyJson = JsString(get = "A string")
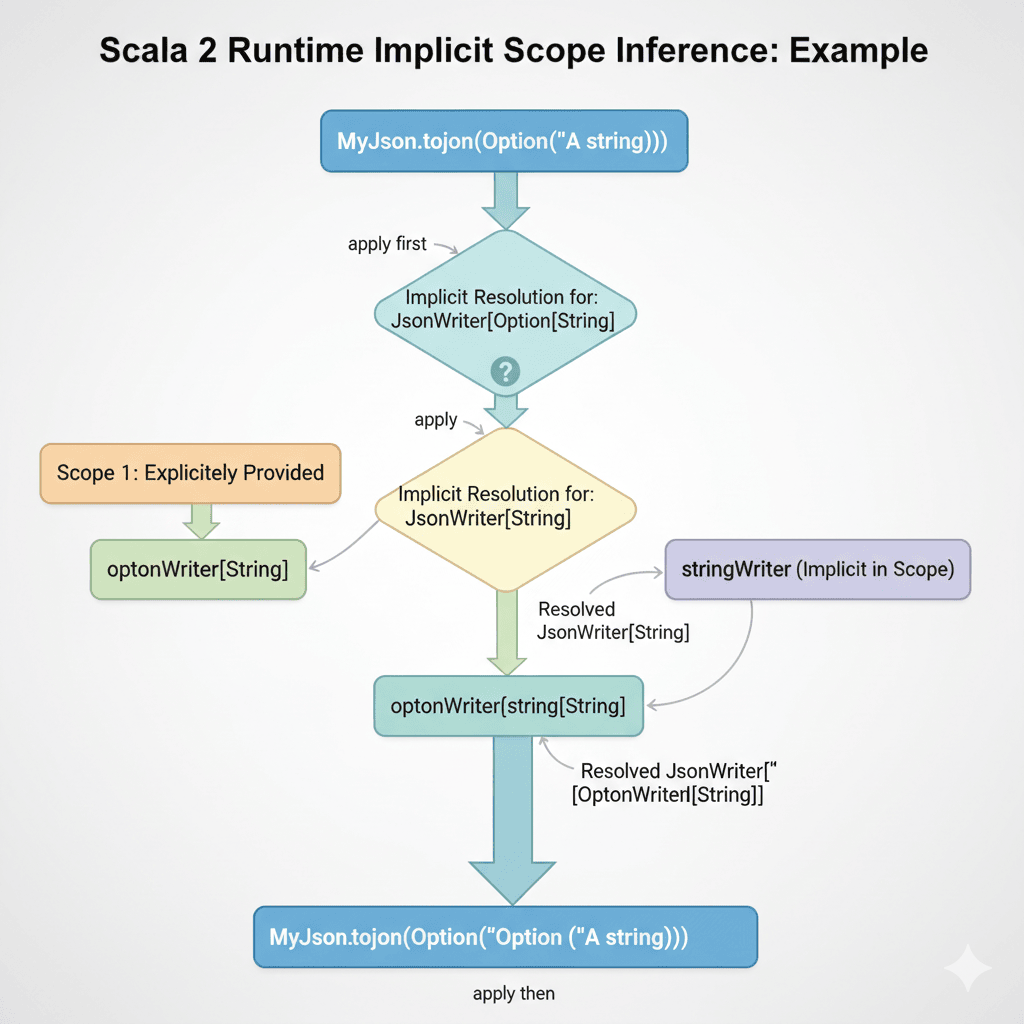
MyJson.toJson(Option("A string"))(optonWriter[String]) // apply first
⬇️
MyJson.toJson(Option("A string"))(optonWriter(stringWriter)) // apply then
implicitmethods with non‐implicit parameters form a different Scala pattern called an implicit conversion, which is an old programming concept.
Key Benefits
- Decoupling: Your data definitions (like
case class Person) are separate from their behaviors (likeShow). - Extensibility: You can add
Showsupport forjava.util.Dateor any other library class without changing its code. - No Inheritance Tax: You don’t need to make all your classes extend a common
Showabletrait, which avoids brittle inheritance hierarchies. - Type-Safe: The compiler guarantees at compile time that the behavior exists for the type you’re using.
(Note: Scala 3 heavily refines this pattern, making it a first-class language feature with given and using clauses, which replace implicits.)
-
Functional Programming in Scala, Ch. 1: “What is functional programming?” → “The benefits of FP: a simple example”, p. 3-12 ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
Category Theory, Ch. 9: “Functors and Natural Transformations” → p. 156-161 ↩
-
Bird & Wadler: Introduction to Functional Programming, Ch. 3: “Lists” → “Map and filter”, p. 61-65 ↩ ↩2 ↩3
-
Programming in Scala Fourth Edition, Ch. 23: “For Expressions Revisited” → p. 528-545 ↩
-
Scala in Depth, Ch. 11: “Patterns in functional programming” → “Currying and applicative style”, p. 266-268 ↩ ↩2
-
Scala with Cats, Ch. 1: “Introduction”, p. 10 -11 ↩

