📝 Research :https://ojitha.blogspot.com.au for my lengthy articles.
Kubernetes Introduction

ip route and crictl. The tutorial examines kube-proxy modes, service discovery via CoreDNS, and the deployment of multi-tier applications using Redis and Nginx. Furthermore, it demonstrates how to expose services using NodePort, scale deployments for high availability, and utilise `kubectl exec` and `cp` for effective pod interaction and troubleshooting.ICIJ Fraud Analysis
Spark Dataset APIs
map and flatMap, and contrasts the standard, untyped join with the type-safe joinWith operation. Furthermore, the guide highlights significant performance considerations for wide transformations, noting that groupByKey requires a full data shuffle and lacks the map-side combine optimisation available in the standard DataFrame groupBy. Finally, the documentation scrutinises a physical query plan to detail how Adaptive Query Execution (AQE) dynamically optimises resource usage by adjusting partition sizes based on runtime statistics.Functional Programming Abstractions in Scala
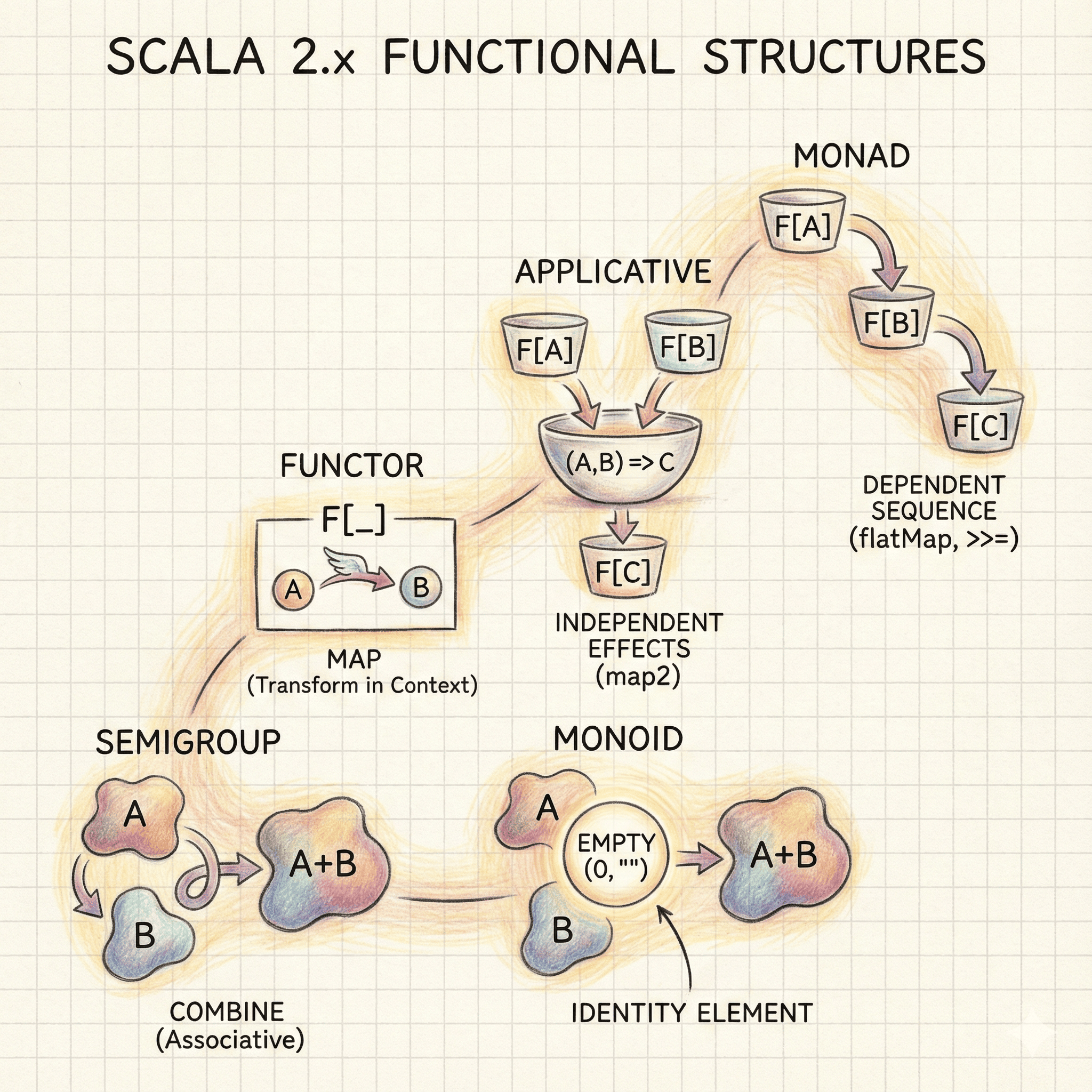
Master the foundation of modern Scala development by exploring five essential functional programming abstractions. This guide takes a deep dive into algebraic structures, starting with Semigroup and Monoid for combining values. It progresses to type constructors, explaining how Functors transform wrapped data, Applicatives combine independent contexts, and Monads sequence dependent computations. By understanding these core patterns, developers can write more polymorphic, composable, and algebraically sound Scala code that works across diverse data types.
Scala 2 Collections explained

Scala collections are a powerful feature providing rich data structures for working with sequences, sets, and maps. The collection hierarchy comprises three main types: Sequence for ordered indexed access, Set for unique elements, and Map for key-value pairs. Scala emphasises immutable collections by default, ensuring thread-safety and referential transparency, while mutable collections enable efficient in-place modifications. Key collection types include List for linked list operations, Vector for random access, and Range for memory-efficient numeric sequences. Understanding the distinction between immutable and mutable collections is essential for writing safe, concurrent Scala code. Iterators enable lazy evaluation, allowing efficient processing of large datasets without consuming memory.